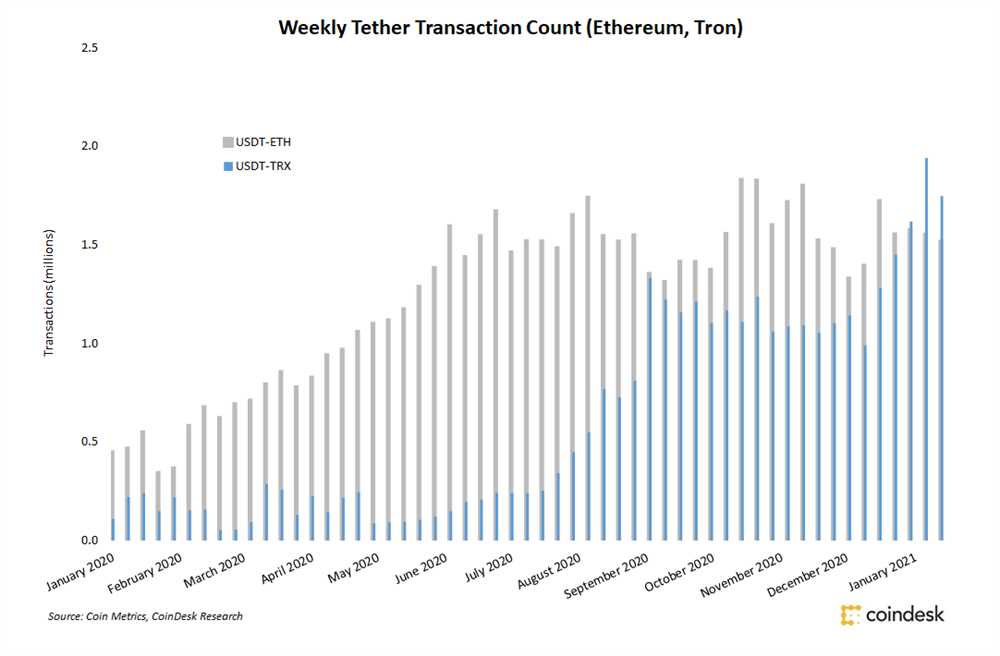
When it comes to using blockchain platforms, one of the most important factors to consider is the fees associated with transactions. Tron, a decentralized blockchain platform, has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its low transaction fees.
In comparison to other blockchain platforms, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, Tron offers a much more cost-effective solution. Bitcoin, for example, is known for its high transaction fees, which can sometimes be a deterrent for users. Ethereum, while more affordable than Bitcoin, still has relatively higher fees compared to Tron.
Tron’s low transaction fees are a result of its efficient consensus mechanism, known as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). This consensus mechanism allows Tron to process transactions at a much faster rate and with lower fees compared to other platforms.
Furthermore, Tron’s low fees make it an attractive option for developers and businesses looking to build decentralized applications (dApps) on the platform. With lower transaction costs, developers can create more affordable and accessible dApps, potentially increasing user adoption.
In conclusion, Tron stands out among other blockchain platforms due to its significantly lower transaction fees. Its efficient consensus mechanism and affordable transaction costs make it an appealing choice for users, developers, and businesses alike.
Tron Fees: An In-Depth Comparison

When it comes to blockchain platforms, one of the key considerations is the fees associated with transactions. Tron, a popular blockchain platform, offers its own unique fee structure that differs from other platforms like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Tron Fee Structure

Tron’s fee structure is designed to be cost-effective and efficient for users. The platform utilizes a system called Bandwidth, which allows users to make transactions without paying any fees. Bandwidth is a resource that is allocated to users based on their TRX holdings. The more TRX a user holds, the more bandwidth they have available to use.
However, if a user exceeds their allocated bandwidth, they will need to pay a fee known as Energy. Energy is another resource that is used to cover additional transaction costs. The cost of Energy is determined by the current market price of TRX.
In addition to Bandwidth and Energy, Tron also charges a small fee called TRX for account creation. This fee helps prevent spam and ensures the integrity of the network. The current fee for account creation is 0.1 TRX.
Comparison to Other Platforms
When compared to other blockchain platforms like Ethereum and Bitcoin, Tron’s fee structure offers several advantages. Ethereum, for example, uses a gas fee system that can be complex and costly for users. The cost of gas on the Ethereum network is determined by market demand, and fees can fluctuate significantly.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, charges a fee for every transaction, regardless of the transaction size. This can make Bitcoin transactions expensive, especially during times of high network activity.
Tron’s Bandwidth and Energy system provides a more predictable and cost-effective fee structure for users. By allocating resources based on TRX holdings, users have more control over their fees and can avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, the low fee for account creation helps maintain the security and efficiency of the Tron network.
In conclusion, Tron’s fee structure offers a competitive alternative to other blockchain platforms. With its Bandwidth and Energy system, Tron provides a cost-effective and efficient way for users to transact on the network while minimizing fees.
Understanding Tron’s Fee System

Tron, a popular blockchain platform, has gained attention for its low transaction fees compared to other blockchain networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin. To understand Tron’s fee system, it’s essential to delve into its unique fee structure and how it differs from other platforms.
Tron’s fee system is designed to support rapid and affordable transactions on its network. Unlike Ethereum, which uses a gas fee model, Tron operates on a bandwidth model. Bandwidth measures the amount of computational resources required to perform a transaction or interact with smart contracts on the Tron blockchain.
To access the Tron network and execute transactions, users need to lock a certain amount of TRX tokens in their wallets as collateral. This TRX acts as a bandwidth resource, determining the user’s available bandwidth and transaction capacity. The more TRX locked in the wallet, the greater the bandwidth allocated.
Tron’s fee system also allows users to freeze their TRX tokens for a specific period to gain additional energy resources. Energy is another important factor that determines transaction costs on the Tron network. By freezing TRX tokens, users can acquire energy resources to execute transactions without spending additional TRX.
The Tron network calculates transaction fees based on the bandwidth and energy consumed for each transaction. The more bandwidth and energy required, the higher the transaction fees. However, Tron’s transaction fees are generally much lower compared to other platforms, making it an attractive choice for decentralized application developers and users.
Tron’s fee system has been praised for its scalability and efficiency. With low transaction fees and high throughput, the Tron network can handle a significant number of transactions per second, making it suitable for applications that require fast and inexpensive transactions.
In conclusion, Tron’s fee system differs from other blockchain platforms like Ethereum by using a bandwidth model. By locking TRX tokens as collateral, users can access bandwidth resources and freeze TRX to gain energy resources. This unique fee structure, along with its scalability, has made Tron a popular choice among developers and users alike.
Tron versus Ethereum: A Fee Comparison

When it comes to comparing the fees on different blockchain platforms, Tron and Ethereum are two popular choices. Both platforms have their own unique fee structures and it’s important to understand the differences before making a decision.
Tron Fees
Tron, also known as TRX, operates on a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism. This means that TRX holders can vote for super representatives who validate transactions on the network. The transaction fees on Tron are paid in TRX and vary depending on the network congestion. On average, Tron transaction fees are significantly lower compared to those on Ethereum.
Tron also has a feature known as energy, which is required to execute smart contracts. Users need to freeze a certain amount of TRX to obtain energy resources, which can then be used to execute smart contracts without incurring additional fees. This makes Tron an attractive choice for developers looking to build decentralized applications (dApps) with low transaction costs.
Ethereum Fees
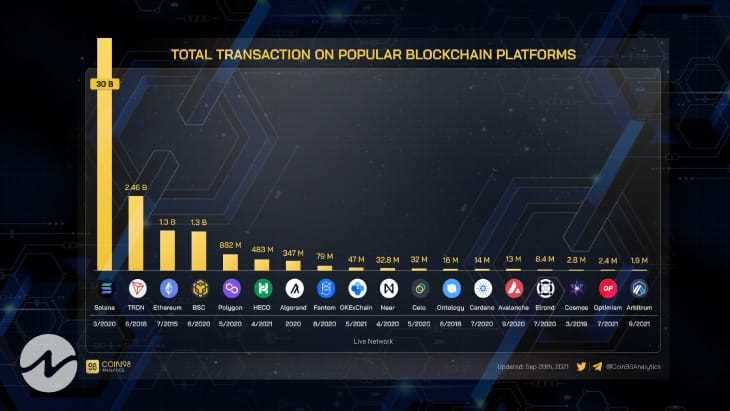
Ethereum, on the other hand, uses a different consensus mechanism called proof-of-stake (PoS). The transaction fees on Ethereum are paid in Ether (ETH) and are determined by the gas limit and gas price. Gas refers to the computational power required to execute a transaction or run a smart contract on the Ethereum network. The gas price is set by users and determines the priority of a transaction.
However, due to the increasing popularity of Ethereum and the limited scalability of the network, transaction fees on Ethereum have been known to spike during times of high demand. This has led to concerns about the sustainability and affordability of using Ethereum for certain applications.
Overall, when comparing Tron and Ethereum in terms of fees, Tron offers lower transaction fees and the ability to execute smart contracts without additional charges through the energy feature. However, Ethereum remains a popular choice due to its established developer ecosystem and larger network. Ultimately, the choice between Tron and Ethereum will depend on the specific use case and individual preferences.
Tron versus Bitcoin: A Fee Comparison
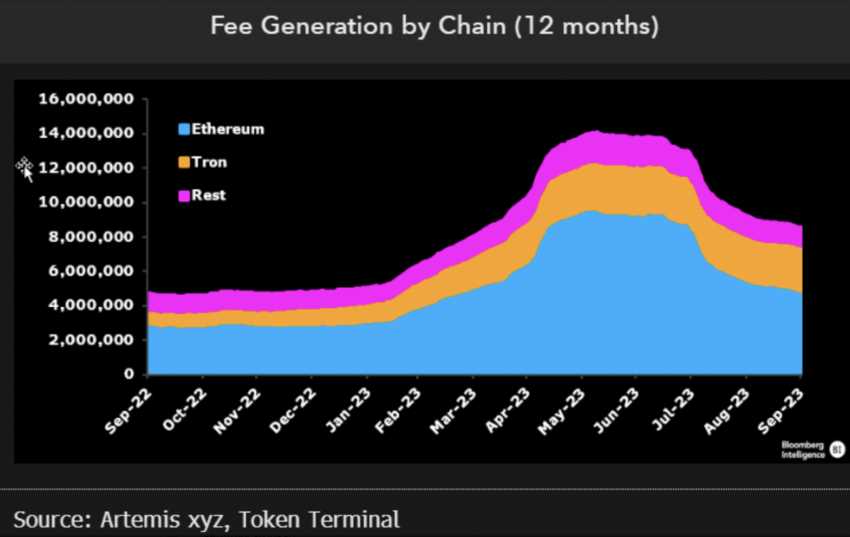
When it comes to comparing transaction fees on different blockchain platforms, it’s important to look at the two major players in the space: Tron and Bitcoin. Both platforms have gained significant popularity and are known for their decentralization and high transaction speeds.
Tron, a blockchain platform founded by Justin Sun, has gained attention for its low transaction fees. On Tron, users can execute transactions with minimal fees, making it an attractive option for those who want to transfer funds quickly and cost-effectively. The fee structure on Tron is designed to be competitive, allowing users to send and receive funds without worrying about high transaction costs.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, has been known for its high transaction fees, especially during times of network congestion. Bitcoin’s fees are determined by a number of factors, such as the size of the transaction and the network’s current demand. As Bitcoin’s popularity has grown, so have its transaction fees, leading to higher costs for users who want to transfer funds on the network.
While Tron offers low transaction fees, Bitcoin’s fees can be significantly higher, especially during peak times. This has led to some users considering alternative blockchain platforms like Tron, which offer faster and more cost-effective transactions. However, it’s important to note that Bitcoin is still the most widely accepted and recognized cryptocurrency, making it a preferred choice for many investors and businesses.
In conclusion, when comparing transaction fees between Tron and Bitcoin, Tron offers a more cost-effective option with its low fees. However, Bitcoin’s widespread acceptance and popularity make it a preferred choice for many despite its higher transaction costs. Ultimately, the choice between Tron and Bitcoin will depend on individual preferences and needs.
Fee Considerations for Developers and Users
When considering which blockchain platform to develop on or use, it is important to take into account the fees associated with transactions. Tron has gained popularity in part due to its relatively low transaction fees compared to other blockchain platforms, which makes it an attractive option for developers and users.
Developers often have to consider the cost of executing smart contracts and deploying decentralized applications (dApps) on blockchain platforms. Tron’s fee structure offers a cost-effective solution, allowing developers to save on transaction fees and allocate their resources more efficiently.
For users, the fees they have to pay to perform transactions can greatly impact their overall experience and adoption of a blockchain platform. High fees can discourage users from participating in transactions and using dApps. Tron’s low fees make it more accessible to a wider range of users and promote higher usage and adoption rates.
However, it is important to note that while Tron’s fees are generally lower compared to other blockchain platforms, the actual fees can vary depending on network congestion and market conditions. It is always advisable for developers and users to stay updated with the current fee structure and factor in potential fluctuations when planning their projects or transactions.
Additionally, developers and users may also need to consider the scalability and transaction speed of a blockchain platform. Tron’s network has been designed to handle a high volume of transactions per second, which contributes to its overall efficiency. This, combined with its low fees, makes Tron an appealing option for developers and users alike.
In summary, when choosing a blockchain platform, developers and users should consider the fees associated with transactions. Tron’s low fees make it a cost-effective option with the potential for higher adoption rates. However, it is important to stay informed about the current fee structure and other factors such as scalability and transaction speed to make informed decisions.
Factors Influencing Tron Fees
Tron (TRX) is a blockchain platform that allows for fast and decentralized transactions. Like any blockchain, Tron charges fees for certain operations on its network. These fees are influenced by several factors, including:
Transaction Type

The type of transaction being performed on the Tron network can affect the fees that users have to pay. For example, sending TRX from one wallet to another typically incurs a different fee than executing a smart contract or interacting with a decentralized application (dApp).
Network Congestion

Similar to other blockchain platforms, Tron fees can be influenced by network congestion. When there is high demand for transactions on the network, the fees tend to increase due to limited block space. Conversely, when network activity is lower, the fees might be lower as well.
Bandwidth and Energy Usage
Tron uses a unique system where users need to freeze some of their TRX tokens to gain bandwidth and energy resources. These resources determine the number of transactions a user can perform and can also influence the fees. The more bandwidth and energy a user requires for their transactions, the higher the fees may be.
Dapp Integration
Tron’s integration with decentralized applications (dApps) also plays a role in determining the fees. Some dApps may have their own fee structures when interacting with their smart contracts or conducting transactions within the dApp. These additional fees might be applied on top of the base Tron fees.
Overall, Tron fees are influenced by transaction types, network congestion, bandwidth and energy usage, and dapp integration. Understanding these factors can help users anticipate and manage their fees when conducting transactions on the Tron network.
What is Tron?
Tron is a blockchain-based platform that aims to decentralize the internet and create a global free content entertainment system.
How do Tron fees compare to other blockchain platforms?
Tron fees are generally much lower compared to other blockchain platforms. Transactions on Tron can be processed at a fraction of the cost of other platforms like Ethereum.
Why are Tron fees lower than other blockchain platforms?
Tron fees are lower due to its unique consensus mechanism called Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), which allows for faster and more affordable transactions compared to other platforms that use Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
Are there any downsides to Tron’s low fees?
While Tron’s low fees are generally seen as a positive aspect, some critics argue that the low fees may attract spam transactions or low-quality content due to the ease of access.