
In the world of blockchain technology, Ethereum, Tron, Solana, and The Block are some of the most prominent and innovative platforms. Each of these platforms offers unique onchain capabilities and benefits, making them essential players in the decentralized finance (DeFi) and cryptocurrency space.
Ethereum, often referred to as the “world computer,” is widely recognized as the pioneer of smart contracts. With its robust and versatile programming language, Solidity, Ethereum allows developers to build and deploy decentralized applications (DApps) with ease. The platform’s expansive ecosystem and large developer community have contributed to its wide adoption and recognition as the go-to platform for DeFi projects.
On the other hand, Tron focuses on providing high-performance and scalability for DApps. Its high throughput and low transaction fees make it an attractive choice for developers seeking to build large-scale applications. Tron’s focus on gaming and entertainment DApps has garnered significant attention and propelled the platform’s growth.
Solana stands out for its impressive scalability, capable of processing thousands of transactions per second. This exceptional throughput makes it suitable for applications that require real-time updates, such as decentralized exchanges and high-frequency trading. Solana’s unique Proof of History (PoH) consensus algorithm further enhances its performance and efficiency.
Lastly, The Block is a decentralized blockchain platform that aims to empower individuals with full control over their data and privacy. With its emphasis on security and anonymity, The Block offers users a secure and private environment to transact and interact with others. Its innovative features, such as zero-knowledge proofs and private smart contracts, ensure that user data remains confidential.
In conclusion, Ethereum, Tron, Solana, and The Block are all trailblazers in the world of blockchain technology. While Ethereum offers a robust and versatile platform for developers, Tron provides high-performance scalability. Solana impresses with its exceptional throughput, and The Block prioritizes privacy and security. Each platform has its own unique onchain capabilities and benefits, contributing to the overall growth and advancement of the blockchain industry.
Exploring the Onchain Capabilities of Ethereum, Tron, Solana, and The Block

Ethereum, Tron, Solana, and The Block are all blockchain platforms that offer unique onchain capabilities. Each platform has its own set of features and benefits that attract developers and users from around the world. By exploring the onchain capabilities of these platforms, we can gain a better understanding of their potential and how they can be utilized in different use cases.
Ethereum:
Ethereum is one of the most well-known blockchain platforms and offers a wide range of onchain capabilities. With its native programming language, Solidity, developers can build smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Ethereum also supports the creation and issuance of digital assets, known as ERC-20 tokens, which have become a standard for tokenization on blockchain. Additionally, Ethereum’s onchain capabilities include decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, such as lending, borrowing, and automated market makers (AMMs), which enable users to interact with financial protocols directly on the blockchain.
Tron:
Tron is another blockchain platform with its own set of onchain capabilities. Similar to Ethereum, Tron supports smart contracts and dApp development. However, Tron differentiates itself by offering higher scalability and faster transaction speeds. Tron also has its own native token, TRX, which can be used for various purposes on the platform. Tron’s onchain capabilities also include the ability to tokenize assets and create digital collectibles, known as non-fungible tokens (NFTs). With Tron’s onchain capabilities, users can engage in gaming, gambling, and content creation on the blockchain.
Solana:
Solana is a high-performance blockchain platform that focuses on scalability and speed. Solana’s onchain capabilities include the ability to process thousands of transactions per second, making it ideal for applications that require fast and efficient processing. Solana utilizes a unique consensus mechanism, called Proof of History, which enables the network to achieve high throughput while maintaining security and decentralization. With Solana, developers can build decentralized applications that require high-performance computing, such as high-frequency trading, decentralized exchanges, and real-time data processing.
The Block:
The Block is not a blockchain platform itself, but it offers a suite of tools and services that enable developers and users to explore and interact with various blockchain networks. The Block’s onchain capabilities include real-time data feeds, blockchain analytics, and integration with external services and protocols. The Block provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to easily navigate and access onchain data, making it a valuable resource for developers and researchers in the blockchain space.
In conclusion, Ethereum, Tron, Solana, and The Block all offer unique onchain capabilities that can be utilized in different ways. Whether it’s building smart contracts and dApps, tokenizing assets, or accessing real-time blockchain data, these platforms provide developers and users with the tools they need to explore the full potential of blockchain technology.
Ethereum: A Platform for Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications
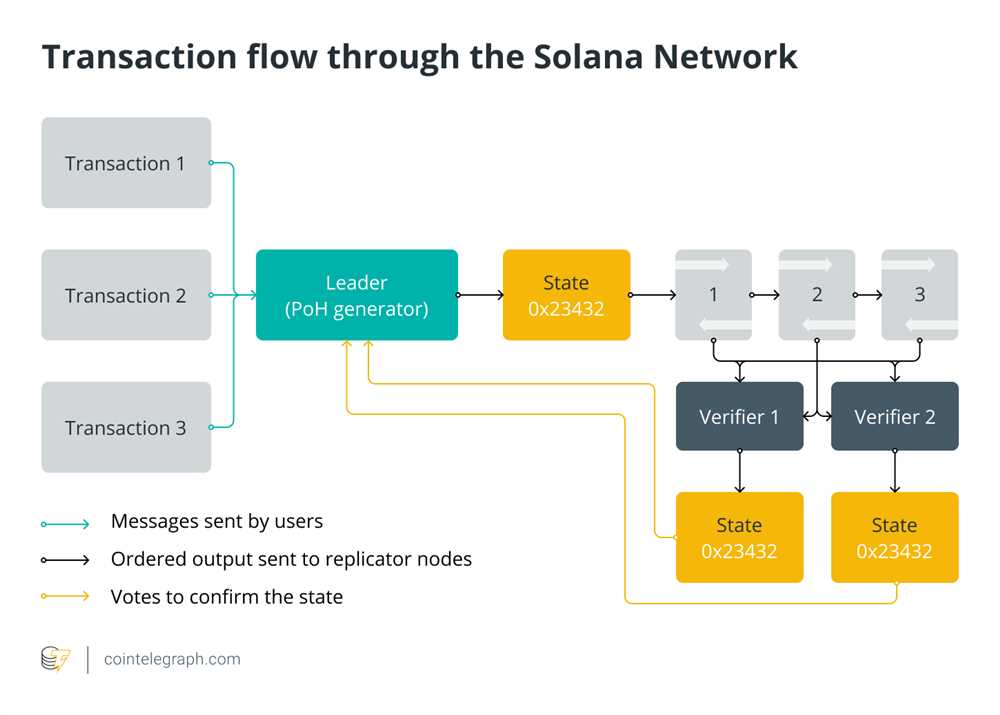
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables the creation and execution of Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps). It was proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin and has become one of the most popular platforms for blockchain development.
At its core, Ethereum is a Turing-complete virtual machine that allows developers to write and deploy smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code. They automatically execute when the predefined conditions are met.
Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), is used as fuel to power the network and execute smart contracts. This ensures that the platform remains secure and prevents it from becoming congested with spam transactions.
Ethereum’s mainnet, or the main Ethereum blockchain, serves as the foundation for a vast ecosystem of decentralized applications. DApps are applications built on top of the Ethereum blockchain that operate in a peer-to-peer manner, without the need for central authorities or intermediaries.
One of the key advantages of Ethereum is its ability to create and manage tokens. Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard has become the industry standard for creating fungible tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. These tokens can represent any digital or physical asset, and their ownership can be easily transferred or traded.
Ethereum’s programmable nature and extensive developer community have led to the creation of a wide range of innovative applications. These include decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, decentralized exchanges, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and much more.
However, Ethereum has faced scalability challenges as its popularity has grown. The network’s current capacity can only handle a limited number of transactions per second, leading to congestion and high transaction fees during periods of high demand.
To address these challenges, Ethereum is undergoing a major upgrade called Ethereum 2.0, which will introduce a new consensus mechanism and improve scalability through the use of shard chains.
In conclusion, Ethereum is a powerful platform for the development of smart contracts and decentralized applications. Its programmable nature, extensive ecosystem, and upcoming upgrades make it a promising choice for developers looking to build innovative blockchain-based solutions.
Tron: Enabling High-Speed Transactions and Scalability

Tron is a blockchain platform that is designed to enable high-speed transactions and scalability. It is built on a unique blockchain architecture that allows for fast and efficient processing of transactions.
One of the key features of Tron is its high throughput capability, which enables it to handle a large number of transactions per second. This is achieved through a combination of innovative technologies, including a delegated proof-of-stake consensus mechanism and optimized network protocols.
In addition to its high-speed transaction processing, Tron also offers scalability by allowing for the creation and implementation of smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This allows for automated and transparent execution of agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs.
With its focus on high-speed transactions and scalability, Tron is well-suited for applications that require fast and efficient processing of transactions, such as decentralized applications (dApps). Tron has also gained popularity in the gaming industry, where it offers a scalable and efficient platform for the development and deployment of blockchain-based games.
Overall, Tron’s high-speed transactions and scalability make it a promising blockchain platform for various industries and applications. Its innovative technologies and focus on efficiency set it apart from other blockchain platforms and enable it to handle the demands of a decentralized and interconnected world.
Solana: Revolutionizing Blockchain Technology with High Throughput and Low Latency
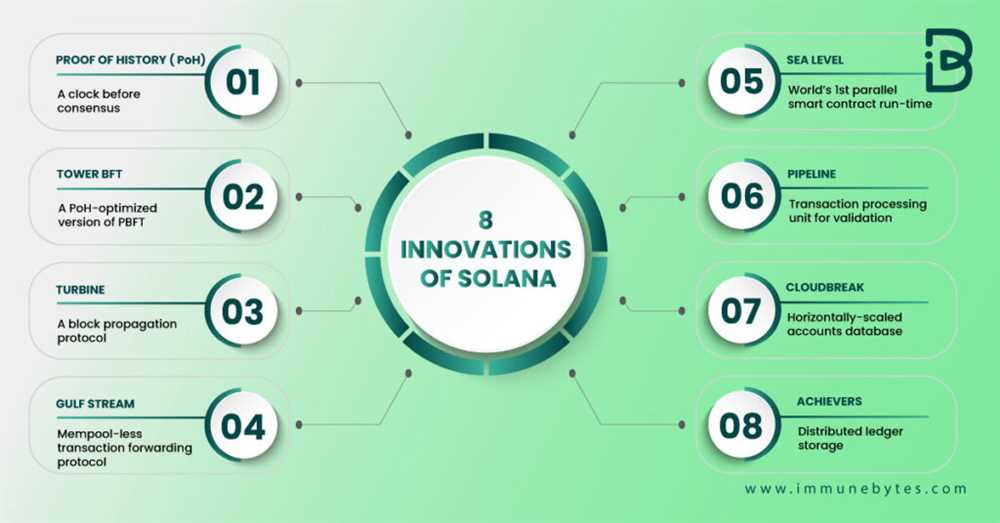
Solana is a blockchain platform that aims to revolutionize the way blockchain technology works by providing high throughput and low latency. It was designed to scale and handle large volumes of transactions quickly and efficiently. Solana’s innovative architecture enables fast transaction processing and high performance, making it an ideal solution for decentralized applications.
High Throughput:
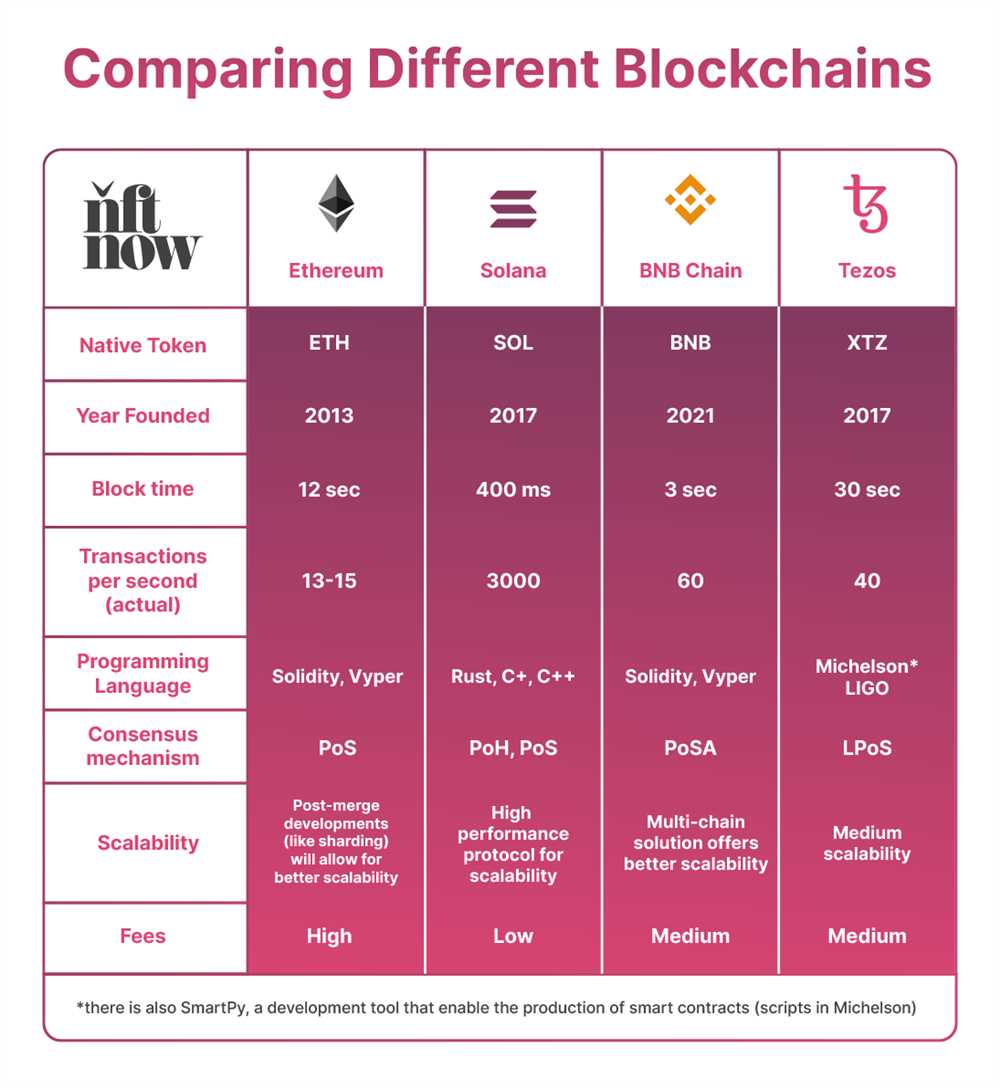
One of the key advantages of Solana is its high throughput capability. Unlike other blockchain platforms, Solana can process thousands of transactions per second, making it one of the fastest blockchain networks in existence. This high throughput is achieved through a combination of a fast consensus algorithm, parallel processing, and a unique architecture that allows for efficient validators communication.
Low Latency:
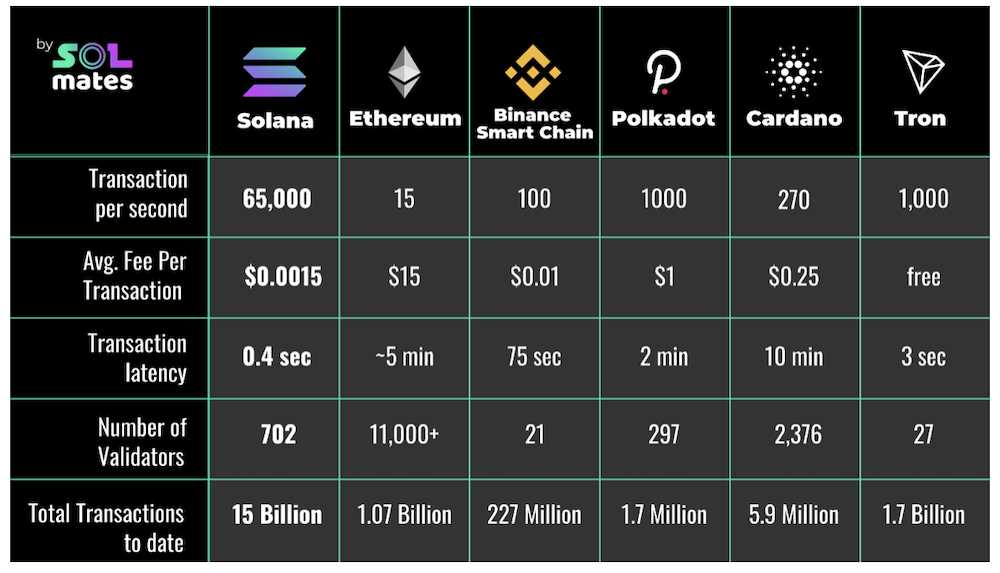
Another important feature of Solana is its low latency, which refers to the time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed. Solana’s low latency is achieved through its fast consensus algorithm, called Proof of History, which allows for quick transaction confirmation. This low latency makes Solana a great choice for applications that require near-instantaneous transaction finality, such as high-frequency trading or real-time gaming.
In addition to its high throughput and low latency, Solana offers other benefits that make it an attractive choice for developers. It has a low transaction cost, making it affordable for users and developers alike. Solana also supports smart contracts, allowing developers to build decentralized applications on the platform. The platform is also highly scalable, meaning it can handle increasing transaction volumes as demand grows.
In conclusion, Solana is revolutionizing blockchain technology with its high throughput and low latency capabilities. Its innovative architecture and fast consensus algorithm enable it to process transactions quickly and efficiently, making it an ideal choice for decentralized applications. With its low transaction cost, support for smart contracts, and scalability, Solana offers a compelling solution for developers looking to build scalable and high-performance blockchain applications.
What are the main onchain capabilities of Ethereum?
One of the main onchain capabilities of Ethereum is its ability to execute smart contracts. Ethereum allows developers to create and deploy decentralized applications (DApps) that can run autonomously without any downtime, censorship, or third-party interference.
What are some benefits of Tron’s onchain capabilities?
Tron provides high scalability and fast transaction speeds, making it suitable for high-volume applications such as gaming and gambling. Additionally, Tron has a growing ecosystem with a large number of decentralized applications, providing users with a wide range of options.
What sets Solana apart in terms of onchain capabilities?
Solana stands out for its high throughput and low latency, allowing it to process a large number of transactions per second. This makes it well-suited for applications that require fast and reliable onchain execution, such as decentralized exchanges and high-frequency trading.
How does The Block enhance onchain capabilities?
The Block is a blockchain data platform that provides comprehensive data and analytics for various blockchains, including Ethereum, Tron, and Solana. Its onchain data capabilities allow users to track transaction history, monitor blockchain activity, and gain insights into network performance.
What are some advantages of Ethereum compared to Tron, Solana, and The Block?
Ethereum has the largest and most established ecosystem among the four. It has a solid track record and a wide range of decentralized applications and protocols built on top of it. Ethereum also has a large developer community and enjoys widespread adoption, making it a popular choice for blockchain-based projects.