
The intricate social dynamics that exist within ape communities have long fascinated researchers and wildlife enthusiasts alike. From the lush rainforests of Borneo to the vast savannahs of Africa, these intelligent creatures have developed complex behaviors and relationships that mirror our own. Studying ape communities not only sheds light on our shared evolutionary history, but also offers valuable insights into the nature of social bonds and cooperation.
At the heart of ape communities lies the importance of strong social bonds, which serve as the foundation for their societal structures. Just like us, apes form close-knit groups consisting of family members and friends. These bonds are often forged through years of companionship, shared experiences, and even grooming rituals. Such relationships provide emotional support, protection, and opportunities for learning and growth.
However, the social dynamics of ape communities are not without their complexities and challenges. Competition for resources, the establishment of hierarchies, and conflicts within groups are all part of the intricate tapestry of ape social life. These dynamics serve as a constant reminder of the delicate balance that exists within their communities and the constant negotiation of individual needs and group cohesion.
Understanding these social dynamics is crucial for conservation efforts and the protection of ape habitats. By gaining insight into their intricate social fabric, we can gain a deeper appreciation for these amazing creatures and work towards sustainable practices that support their communities.
Understanding Ape Society

Apes are highly social animals that live in complex communities. By studying the social dynamics of ape societies, researchers can gain valuable insights into the nature of human social behavior.
Social Structure
Ape societies are typically organized into hierarchical structures, with dominant individuals at the top and subordinate individuals below. These hierarchies are based on a combination of physical strength, social skill, and sometimes alliances.
Within ape societies, there are also defined units, such as family groups or bands, which consist of related individuals. These units play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining social bonds.
Communication

Communication is a vital aspect of ape society. Apes use various forms of communication, including vocalizations, facial expressions, and body postures. These forms of communication help to establish and maintain social relationships, convey information about resources, and mediate conflicts.
Apes have also been observed using gestures and signs to communicate with each other. For example, they may use a specific gesture to request food or indicate aggression. This ability to communicate through gestures highlights the complex and sophisticated nature of ape social interactions.
Cooperation and Altruism

Cooperation and altruism are important elements of ape society. Some forms of cooperation include hunting together, sharing food, and protecting each other from threats. These cooperative behaviors serve to strengthen social bonds within the group and promote overall group cohesion.
Furthermore, apes have been observed displaying altruistic behaviors, such as consoling distressed group members or providing care for young individuals that are not their own offspring. These acts of altruism demonstrate a higher level of empathy and social understanding within ape societies.
Understanding the dynamics of ape society is crucial for gaining insights into the evolution of social behavior in humans. By studying the social interactions, communication, and cooperation within ape communities, researchers can shed light on the origins of human social complexity and the driving forces behind our own social behavior.
| Ape Societies | Social Dynamics | Communication | Cooperation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical structures | Establishing and maintaining social bonds | Vocalizations, facial expressions, body postures | Cooperation in hunting, sharing food, protection |
| Family groups | Gestures and signs | Altruistic behaviors | Empathy and social understanding |
The Role of Hierarchy in Ape Communities
In the complex social dynamics of ape communities, hierarchy plays a crucial role in structuring and maintaining order within the group. While it may seem counterintuitive, a hierarchical system can actually foster social cohesion and reduce conflict among individuals.
Establishing Dominance

Within ape communities, a hierarchy is formed through various means. Dominance is established through displays of physical strength, aggression, and posturing. The most dominant individual in the group assumes the highest rank, while others fall into their respective positions.
This hierarchical structure provides clear roles and expectations for each individual within the community. Those lower in rank understand their place and role within the group, reducing the likelihood of constant power struggles and conflict.
Social Benefits
The hierarchy within ape communities offers social benefits to both dominant and subordinate individuals. Dominant individuals typically have priority access to resources such as food, mates, and shelter. In return, they provide protection and ensure the well-being of the group as a whole.
Subordinate individuals benefit from the stability and protection provided by the dominant members. They often gain access to resources through alliances and affiliations with higher-ranking individuals. Additionally, the hierarchical structure also helps to prevent inbreeding, as dominant individuals may restrict access to mating partners to maintain genetic diversity within the community.
| Roles | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Dominant individuals | Access to resources, protection, maintenance of group cohesion |
| Subordinate individuals | Stability, resource access through alliances, prevention of inbreeding |
In summary, hierarchy plays a vital role in ape communities by establishing order and reducing conflict. It provides clear roles and expectations for individuals, ensures the distribution of resources, and promotes the overall well-being of the group. Understanding the importance of hierarchy in ape communities can provide valuable insights into the social dynamics of other animal species as well as human societies.
Communication and Cooperation Among Apes
Apes utilize a sophisticated system of communication to interact and cooperate with one another. This complex communication plays a vital role in building and maintaining social bonds within ape communities.
Types of Communication

Apes communicate through a variety of methods, including vocalizations, gestures, and body movements. Vocalizations, such as hoots, grunts, and screams, are used to convey information and express emotions. Gestures, like arm movements and facial expressions, are also important means of communication for apes. Through body movements like grooming, touching, and hugging, apes are able to establish and strengthen social bonds.
Cooperation and Collaboration
Apes engage in cooperative behaviors that are essential for their survival and well-being. They work together to accomplish tasks such as foraging for food, building shelters, and defending their territories. This collaboration relies on effective communication to coordinate their efforts and distribute roles and responsibilities.
Apes display cooperation in various contexts, including hunting and sharing food resources. They communicate and coordinate their actions to strategize and maximize their chances of success. Cooperation also extends to raising offspring, where apes assist each other in parenting duties, providing protection and support for the young.
In many cases, cooperation among apes is based on reciprocity. They engage in reciprocal behavior, where individuals take turns assisting each other or sharing resources. This reciprocity helps maintain social bonds and fosters cooperation within the community.
Overall, communication and cooperation are fundamental aspects of ape social dynamics. By effectively communicating and collaborating, apes are able to build strong social bonds, ensure their survival, and thrive within their communities.
Social Learning and Cultural Exchange in Ape Communities

Social learning plays a crucial role in ape communities, allowing individuals to acquire knowledge and skills from their peers. Ape communities are known for their complex social structures, which provide opportunities for cultural exchange and the transmission of learned behaviors.
Types of Social Learning
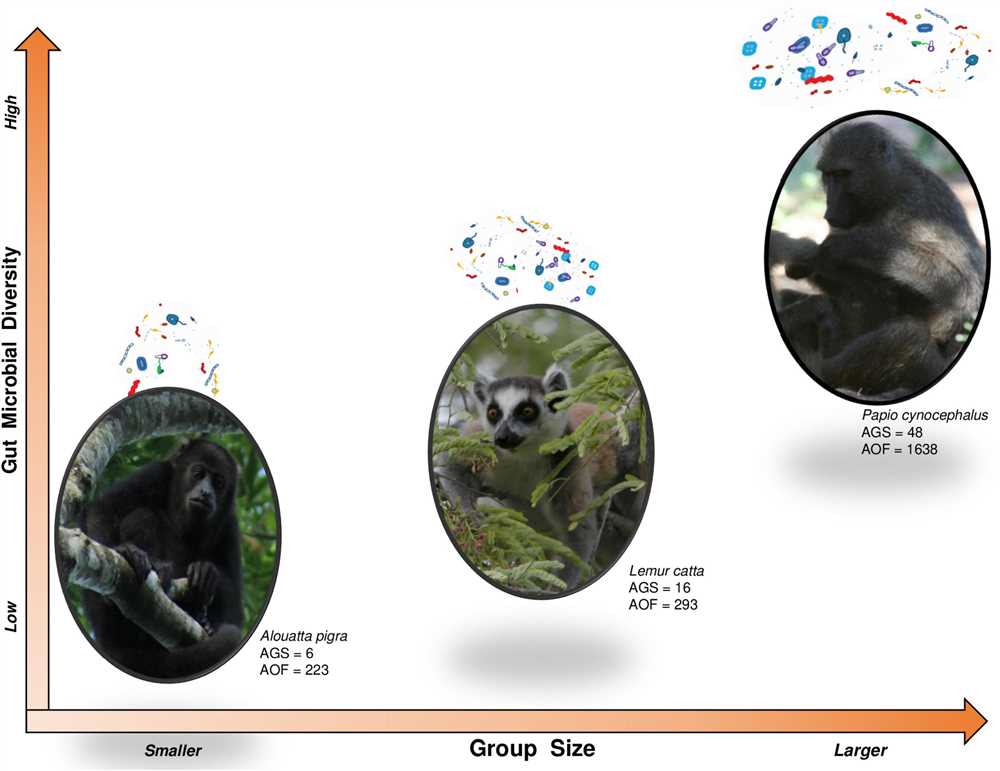
There are several types of social learning that occur within ape communities. One type is observational learning, where individuals observe and imitate the actions of others. This type of learning is particularly important for acquiring complex behaviors, such as tool use or foraging techniques.
Another type of social learning is teaching, where experienced individuals actively guide and instruct younger or inexperienced individuals. Teaching involves a higher level of interaction and communication, and it allows for the transmission of cultural knowledge and traditions from one generation to the next.
Cultural Exchange in Ape Communities
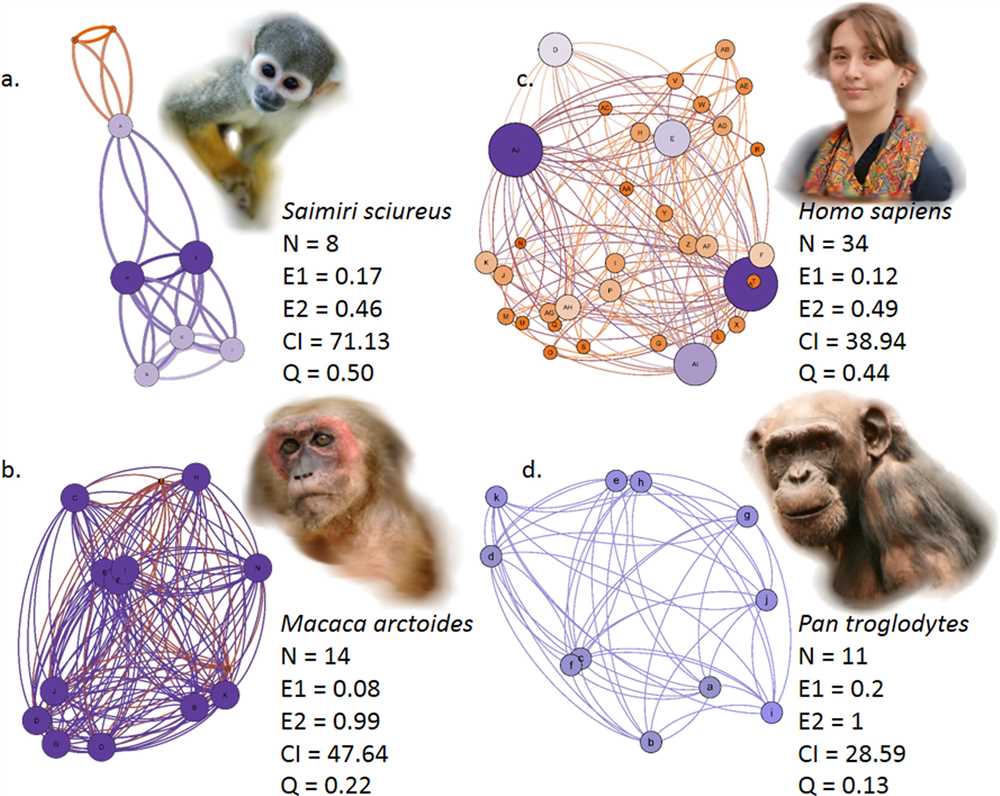
Ape communities also engage in cultural exchange, where different groups or individuals share and adopt behaviors from each other. This cultural exchange can occur through intergroup interactions or when individuals move between groups, bringing with them their own learned behaviors.
Studies have shown that cultural exchange in ape communities can lead to the spread of innovative behaviors, as individuals adopt and modify behaviors they observe in others. This exchange of cultural knowledge contributes to the diversity and adaptability of ape communities, allowing them to thrive in a changing environment.
In conclusion, social learning and cultural exchange are fundamental processes in ape communities. Through observation, teaching, and cultural exchange, apes are able to acquire knowledge and skills from one another, leading to the development and transmission of complex behaviors. Understanding these social dynamics is important for conservation efforts and for gaining insights into the evolution of social learning in our own human ancestors.
How do apes form social bonds within their communities?
Apes form social bonds within their communities through various means, such as grooming, playing, and sharing food. These activities help to strengthen the relationships between individuals and promote cooperation and social cohesion within the group.
What role does grooming play in ape communities?
Grooming plays a crucial role in ape communities as it serves multiple functions. It not only helps in maintaining personal hygiene by removing parasites and dirt from the fur, but also serves as a social bonding activity. Grooming sessions provide opportunities for individuals to interact, build trust, and establish social hierarchies within the group.
Are there any similarities between the social dynamics of ape communities and human societies?
Yes, there are several similarities between the social dynamics of ape communities and human societies. Like humans, apes engage in complex social behaviors, such as cooperation, competition, and forming alliances. They also exhibit emotional intelligence and empathy, which are integral to building and maintaining social relationships. Additionally, both apes and humans have hierarchies within their societies, with dominant individuals having more influence and access to resources.
What are the benefits of strong social bonds within ape communities?
Strong social bonds within ape communities provide several benefits. First, they promote cooperation and help in resource sharing, as individuals are more likely to share food and provide assistance to their bonded partners. Second, social bonds aid in conflict resolution, as individuals with strong relationships are more likely to resolve disputes peacefully. Finally, strong social bonds contribute to the overall well-being and mental health of individuals, as they provide a sense of support, security, and belonging.