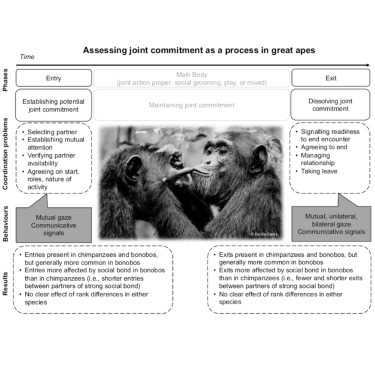
The intricate web of social connections that exist among apes is a fascinating subject of study. These intelligent creatures, known for their close genetic relationship to humans, exhibit a remarkable array of behaviors and interactions that highlight the importance of social bonds. From grooming rituals to cooperative hunting, apes rely on their ability to form strong social connections to survive and thrive in their complex environments.
One of the most remarkable aspects of ape societies is their ability to build bridges between individuals and groups. These bridges serve as a means of communication, cooperation, and support, allowing apes to navigate the challenges of their environment more effectively. Whether it is a mother teaching her offspring how to forage for food or a group of individuals banding together to defend their territory, the bonds forged among apes are a testament to their social intelligence and adaptability.
Within ape communities, the strength in numbers is undeniable. The collective knowledge and experience accumulated by a group of apes can be leveraged to overcome obstacles and find new opportunities. This collective intelligence is often observed in the collaborative activities of apes, such as coordinated hunting or the sharing of resources. It is through these collective efforts that apes are able to succeed in tasks that an individual would find challenging or even impossible.
Moreover, the social bonds among apes have a deeper significance than just survival. These bonds serve as a source of emotional support and companionship. Apes have been observed engaging in playful interactions, comforting each other in times of distress, and displaying gestures of affection. These social connections provide apes with a sense of belonging and contribute to their overall well-being.
In conclusion, the social bonds among apes are a remarkable aspect of their behavior and deserve further exploration. By studying the intricate web of connections within ape communities, we can gain insights into the complexities of social relationships and the potential strength that lies in numbers. Understanding the social dynamics of apes not only sheds light on our own evolutionary history but also deepens our appreciation for the diversity of life on Earth.
The Importance of Social Bonds

Social bonds play a crucial role in the lives of apes, as they provide a sense of security, support, and cooperation within their communities. These bonds are developed through various social interactions, such as grooming, playing, and sharing resources.
1. Emotional Support:
Apes rely on social bonds to provide emotional support and comfort in times of distress. They show empathy towards one another, offering reassurance and physical contact to reduce stress and anxiety. This emotional support helps strengthen the overall well-being of the individuals and reinforces their social connections.
2. Cooperation and Collaboration:
Social bonds enable apes to engage in cooperative behaviors and collaborative activities, such as hunting for food or raising their young. By working together, apes can achieve common goals and increase their chances of survival. These cooperative efforts are facilitated by their social bonds, which foster trust and effective communication among group members.
3. Conflict Resolution:
Social bonds also play a vital role in resolving conflicts among apes. Through social interactions, such as reconciliation or mediation, apes are able to restore peace within their communities and maintain harmonious relationships. These conflict resolution strategies rely on the strength of their social bonds and their ability to empathize and forgive.
4. Knowledge Sharing:
Social bonds facilitate the sharing of knowledge and skills among apes. Older and experienced individuals pass on their wisdom and expertise to younger members of the group, ensuring the transmission of essential survival techniques and cultural traditions. This knowledge sharing strengthens the overall resilience and adaptability of the community.
In conclusion, social bonds are of paramount importance for apes, as they provide emotional support, facilitate cooperation and collaboration, aid in conflict resolution, and enable knowledge sharing. These social interactions, built on trust and empathy, contribute to the well-being and survival of apes, highlighting the significance of their social bonds in establishing strong communities.
Communication and Cooperation Among Apes

Apes, such as chimpanzees, bonobos, gorillas, and orangutans, possess fascinating abilities in communication and cooperation that have been studied extensively by scientists. These primates actively use various forms of communication to maintain social bonds and coordinate group activities.
One important aspect of communication among apes is vocalization. They produce a variety of vocal sounds, including calls, grunts, and screams, which serve different purposes. For example, chimpanzees use different calls to warn others of predators or to signal the presence of food sources.
In addition to vocalization, apes also rely on body language, facial expressions, and gestures to convey their intentions and emotions. They can use facial expressions such as smiles, frowns, and bared teeth to display dominance or submission. They also use gestures such as pointing or reaching to request assistance or to share objects.
Cooperation is another important aspect of ape social behavior. Apes engage in cooperative activities such as hunting, food sharing, and grooming. They work together to achieve common goals, leveraging their social bonds and cognitive abilities. For example, chimpanzees engage in coordinated hunting, where individuals collaborate to capture and share prey.
Apes also engage in reciprocal altruism, where they help others without immediate benefit to themselves. This behavior strengthens social bonds and promotes cooperation within the group. Apes have been observed to share food, groom each other, and offer comfort in times of distress.
The ability of apes to communicate and cooperate has been linked to their intelligence and social cognition. They possess complex mental abilities, including theory of mind, which allows them to understand and interpret the intentions, desires, and beliefs of others. This understanding enables them to cooperate and coordinate their actions effectively.
In conclusion, communication and cooperation are crucial aspects of ape social behavior. Through vocalization, body language, and gestures, they communicate with each other, maintain social bonds, and coordinate group activities. Their ability to cooperate and engage in reciprocal altruism highlights the significance of social bonds in their lives.
Challenges in Maintaining Social Bonds

Building and maintaining social bonds among apes is crucial for their well-being and survival. However, there are several challenges that apes face in maintaining these social bonds:
1. Limited Resources:
One of the major challenges apes face is the limited availability of resources such as food, water, and shelter. This scarcity can lead to competition and conflict among individuals, making it difficult to maintain social bonds.
2. Hierarchy and Dominance:

Apes, like humans, establish social hierarchies within their groups. Dominant individuals often have priority access to resources and mates, which can create tension and disrupt social bonds.
3. Environmental Changes:
Changes in the environment, such as deforestation and habitat loss, can disrupt the social dynamics among apes. Displacement from their natural habitats can lead to the fragmentation of groups and the loss of social bonds.
4. Inter-group Competition:
Apes living in overlapping territories may engage in inter-group competition for resources, leading to conflicts and the weakening of social bonds. These competitions can sometimes escalate to violent encounters.
5. Human Impact:
Human activities, including habitat destruction, hunting, and the illegal pet trade, pose significant challenges to the social bonds of apes. The loss of family members or entire groups due to human intervention can have a profound impact on the social dynamics and relationships among apes.
Despite these challenges, apes have shown remarkable resilience in maintaining their social bonds. Through communication, cooperation, and adaptive behaviors, they continue to form strong social connections that are vital for their survival.
The Power of Numbers
When it comes to social bonds among apes, the power of numbers cannot be underestimated. Apes, like humans, are highly social creatures and form intricate social networks within their communities. These networks are strengthened by the sheer number of individuals present, as larger groups provide more opportunities for social interaction and support.
Research has shown that larger groups of apes tend to have more stable social structures, with individuals forming long-lasting bonds and alliances. This is because living in larger groups allows for a greater diversity of relationships, providing individuals with a wider range of companions and allies.
In addition, larger groups create a sense of security and protection. In the face of threats from predators or other external forces, having a larger group can increase the chances of survival. Apes in larger groups can rely on the collective knowledge and skills of their peers, enabling them to adapt and respond effectively to changing environments.
The power of numbers also extends to the sharing of resources. In larger groups, there are more individuals available to locate and exploit food sources. This increases the chances of finding sufficient food for everyone, reducing the competition and potential for conflict.
Furthermore, living in larger groups can enhance social learning and cultural transmission. With more individuals present, there is a greater pool of knowledge and experiences to draw from. Apes can learn from one another, passing on knowledge and skills across generations. This collective learning allows apes to continually improve and innovate, contributing to the overall success and survival of the group.
In conclusion, the power of numbers plays a significant role in the social bonds among apes. Larger groups provide more opportunities for social interaction, support, and the formation of long-lasting bonds. They also offer increased security, resource availability, and opportunities for social learning. Understanding the power of numbers is crucial in studying the behavior and dynamics of ape communities.
How do social bonds among apes contribute to their survival?
Social bonds among apes play a crucial role in their survival. These bonds allow them to cooperate and work together to find food, defend against predators, and care for their young. By building strong social bonds, apes are able to rely on each other for support, which increases their chances of survival.
What are some examples of social behaviors observed among apes?
Apes are known for their complex social behaviors. Some examples include grooming, which helps to strengthen social bonds and remove parasites, and cooperative hunting, where multiple apes work together to catch small animals. They also engage in social play, which helps to develop social skills and establish hierarchy within the group.
Do all apes form social bonds?
Yes, all apes form social bonds to some extent. However, the strength and complexity of these bonds can vary between species. For example, chimpanzees are known to have highly complex social structures with strong bonds between individuals, while orangutans have more solitary lifestyles and form weaker social bonds.
How do social bonds among apes compare to those among humans?
The social bonds among apes and humans share some similarities, as both species rely on social interaction for survival and well-being. However, there are also important differences. Humans have developed complex language skills and cultural systems that greatly influence their social bonds, while apes primarily rely on nonverbal communication and simpler forms of social interaction.