
As the world of decentralized finance continues to grow, more and more users are flocking to the Tron network. Tron, known for its high-speed transactions and low fees, has gained popularity among users looking for a seamless and cost-effective way to transact.
But what exactly are Tron gas fees? And why do users need to understand them?
Tron gas fees are the cost associated with executing transactions and smart contracts on the Tron network. Similar to gas fees on other blockchain networks, Tron gas fees help incentivize miners to validate and process transactions.
It’s important for every user to understand Tron gas fees because they directly impact the cost and speed of transactions. By understanding how gas fees are calculated and why they vary, users can make informed decisions to optimize their transaction experience on the Tron network.
What are Tron Gas Fees?

Tron gas fees are a fundamental aspect of the Tron blockchain network. Similar to other blockchain protocols, such as Ethereum, gas fees are used to ensure the efficiency and security of transactions on the Tron network.
Gas fees are the costs associated with processing and executing transactions, smart contracts, and other operations on the Tron blockchain. These fees are denominated in TRX, the native cryptocurrency of the Tron network.
When a user initiates a transaction or interacts with a smart contract on Tron, they must pay a specific amount of gas fees. The complexity and computational resources required for the transaction or operation determine the gas fees.
How are Tron Gas Fees Calculated?

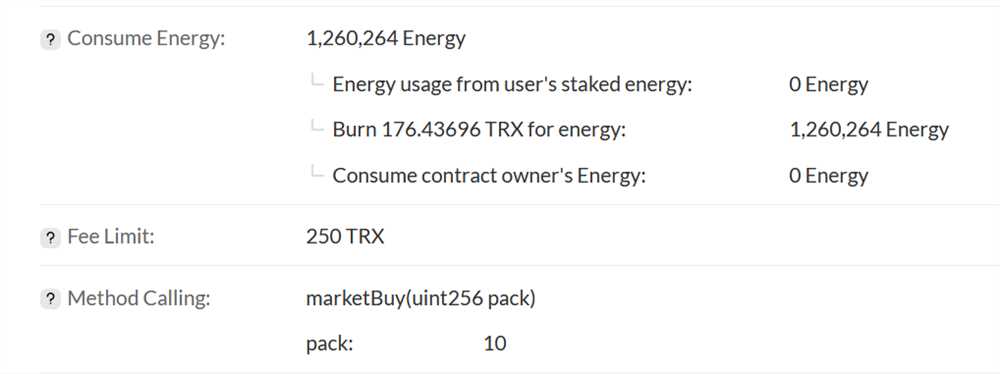
Tron gas fees are determined by multiplying the total amount of computational resources utilized by the transaction or operation with the current gas price. The gas price is measured in Sun, which is the smallest unit of TRX.
It’s important to note that Tron gas fees are dynamic and can vary based on network congestion and demand. During times of high network activity, gas fees may increase due to increased competition for computational resources.
Tron gas fees are deducted from the user’s wallet balance when a transaction or operation is initiated. If the wallet balance does not have sufficient funds to cover the gas fees, the transaction or operation may fail.
Why are Tron Gas Fees Important?
Tron gas fees play a crucial role in maintaining the security and efficiency of the network. They serve as a measure to prevent spam attacks and allocate computational resources to the most essential transactions and operations.
Gas fees also influence the speed at which transactions are processed on the Tron network. Higher gas fees often result in faster confirmation times, as miners are incentivized to prioritize transactions with higher fees.
Furthermore, gas fees provide an economic model for sustaining the Tron network. Validators and miners are rewarded with gas fees for their role in processing transactions and securing the network.
Understanding Tron gas fees is essential for users who want to effectively participate in the Tron ecosystem. By monitoring gas fees and adjusting gas prices, users can optimize transaction speed and cost.
Overall, Tron gas fees are a critical component of the Tron network, ensuring its security, efficiency, and sustainability.
How Tron Gas Fees are Calculated
Tron gas fees are calculated based on several factors. The main factors include the complexity of the transaction, the current network congestion, and the amount of resources required to execute the transaction.
The complexity of the transaction refers to the number of operations and the amount of computational power required to complete the transaction. Transactions that involve complex calculations or multiple operations will generally have higher gas fees.
Network congestion is another important factor in gas fee calculation. When there are many transactions being processed on the network, the gas fees tend to increase. This is because there is a limited amount of computational power available to process transactions, and as demand increases, the gas fees rise to prioritize transactions based on the fees paid.
The amount of resources required to execute the transaction is also taken into account when calculating gas fees. This includes factors such as the amount of data being processed and the storage required for the transaction. Transactions that require more resources will generally have higher gas fees.
Overall, the gas fees for a Tron transaction are calculated to reflect the resources and computational power required to execute the transaction, as well as the current network conditions. By considering these factors, users can better understand and plan for the gas fees associated with their transactions on the Tron network.
Why Tron Gas Fees Matter to Users
Tron gas fees play a crucial role in the Tron network and have a direct impact on its users. Understanding and managing these fees is important for anyone interacting with the Tron blockchain. Here are some key reasons why Tron gas fees matter:
1. Transaction Costs: Gas fees represent the cost of executing transactions on the Tron blockchain. Just like any other network, Tron requires computational resources to process and validate transactions. Users must pay gas fees to compensate for these resources, ensuring smooth and reliable transactions.
2. Network Congestion: Gas fees also help manage network congestion. When the network is busy with a high volume of transactions, gas fees increase to prioritize and incentivize miners to validate transactions. This mechanism helps maintain the integrity and efficiency of the Tron network.
3. Resource Allocation: Tron gas fees help allocate computational resources fairly among users. By charging fees, the network ensures that users who require a higher volume of resources, such as executing complex smart contracts, contribute more to the network’s maintenance and operations.
4. User Experience: Gas fees impact the overall user experience on the Tron network. Higher gas fees can result in more expensive transactions and longer confirmation times. Users need to consider gas fees when deciding on the urgency and priority of their transactions.
5. Network Sustainability: Gas fees play a critical role in ensuring the long-term sustainability of the Tron network. By charging fees, the network can support ongoing development, security, and upgrades, which are essential for its growth and success.
Overall, Tron gas fees are an integral part of the Tron blockchain ecosystem. Understanding their importance and managing them effectively can help users make informed decisions and navigate the network with confidence.
Tips for Reducing Tron Gas Fees
Tron gas fees can sometimes be a nuisance, but there are several tips you can follow to reduce them and save money. Here are some strategies you can try:
1. Optimize Your Smart Contracts
One way to reduce Tron gas fees is by optimizing your smart contracts. Consider optimizing and refactoring your code to make it more efficient and minimize the number of instructions and calculations. This can help reduce the amount of gas consumed and lower transaction costs.
2. Use Off-Peak Hours
Gas fees on the Tron network can vary based on network congestion. Make use of off-peak hours, when the network is less congested, to perform your transactions. This can help you save money by taking advantage of lower gas fees during these periods.
3. Combine Transactions

Instead of making multiple small transactions, consider combining them into a single transaction. This can help reduce the overall gas fees, as you will only need to pay for a single transaction instead of multiple ones.
4. Choose the Right Gas Price

When submitting a transaction, you have the option to choose the gas price. Higher gas prices result in faster confirmation times, but they also come with higher fees. Analyze the network conditions and choose a gas price that provides a good balance between confirmation time and cost.
5. Use Tron-side Solutions

Consider utilizing Tron-side solutions, such as sidechains or layer 2 protocols, to offload some of your transactions. Offloading to these solutions can help reduce gas fees and improve scalability.
By following these tips, you can effectively reduce your Tron gas fees and save money in the process. Remember to stay up to date with the latest developments in the Tron ecosystem, as new solutions and optimizations may become available over time.
What are Tron gas fees?
Tron gas fees are the costs associated with executing transactions and running smart contracts on the Tron blockchain. These fees are paid in the native cryptocurrency of Tron, which is TRX.
How are Tron gas fees calculated?
Tron gas fees are calculated based on the complexity of the transaction or smart contract being executed. The more complex the operation, the higher the gas fee. Gas fees are also influenced by network congestion and market demand.
Can Tron gas fees be avoided?
No, Tron gas fees cannot be completely avoided. However, users can minimize their gas fees by optimizing their transactions and smart contracts for efficiency. This includes writing efficient code and using the appropriate gas limit and gas price.
What happens if I don’t pay the required Tron gas fee?
If you don’t pay the required Tron gas fee, your transaction or smart contract execution will fail. The transaction or operation will not be processed by the network, and you will not achieve the desired outcome. It is important to pay the necessary gas fees to ensure the success of your transactions and operations.