
Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, two platforms have emerged as frontrunners: Tron Network and Ethereum. These platforms have revolutionized the way we transact, create decentralized applications, and tokenize assets. However, each platform has its unique features and philosophies, making them stand out in their own right. In this comparative analysis, we will take an in-depth look at Tron Network and Ethereum, exploring their similarities, differences, and their potential to shape the future of decentralized finance.
Tron Network:
The Tron Network, founded by Justin Sun, is a decentralized blockchain platform that aims to create a global digital content entertainment system. Tron’s main objective is to eliminate intermediaries and empower content creators by enabling them to directly interact with their audience. With a focus on scalability and high-speed transactions, Tron implements a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which allows for faster block confirmation and greater transaction throughput. Tron’s native cryptocurrency, TRX, fuels the network and acts as a medium of exchange for services and products within the Tron ecosystem.
Ethereum:
Ethereum, created by Vitalik Buterin, is widely regarded as the pioneer of smart contract and decentralized application (dApp) development. Ethereum’s main goal is to provide a platform for developers to build and deploy applications without the need for centralized intermediaries. Ethereum utilizes a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which ensures the security and immutability of its blockchain. The native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, Ether (ETH), is used as fuel to execute smart contracts and power dApps on the network.
Comparison:
When comparing Tron Network and Ethereum, both platforms share the common goal of decentralization and empowering developers. However, they differ in their underlying technologies and design philosophies. Tron Network offers faster transaction speeds and greater scalability due to its DPoS consensus mechanism, while Ethereum provides a more secure and battle-tested network through its PoW consensus mechanism.
In terms of adoption and user base, Ethereum has a significant head start, with a large and vibrant community of developers and users. This enables a broader range of dApps and projects on the Ethereum network. Tron Network, on the other hand, has gained popularity in the gaming and gambling industries, where its high transaction throughput and low fees cater to the needs of these specific use cases.
Conclusion:
Tron Network and Ethereum are two leading blockchain platforms that have transformed the decentralized landscape. While Ethereum excels in security and adoption, Tron Network focuses on speed and scalability. Both platforms have their strengths and weaknesses, and their success ultimately depends on their ability to address the needs of developers and users. As the blockchain industry continues to evolve, it will be fascinating to see how these platforms shape the future of decentralized finance and contribute to the wider adoption of blockchain technology.
Overview of Tron Network
Tron Network is a blockchain-based decentralized platform for building and deploying smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It was founded by Justin Sun in 2017 with the goal of revolutionizing the entertainment industry by creating a platform that enables direct content sharing between creators and consumers, without the need for intermediaries.
The Tron Network operates on its native cryptocurrency called TRX, which is used for transaction fees, staking, and voting within the network. The platform incorporates a consensus mechanism called Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), which allows token holders to participate in the block production process and validate transactions.
One of the key features of Tron Network is its high scalability, capable of handling thousands of transactions per second. This is achieved through the implementation of an optimized version of the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) called the Tron Virtual Machine (TVM).
Additionally, Tron Network offers a wide range of tools and resources for developers to build and deploy their own dApps. It supports various programming languages such as Java and Solidity, making it accessible to a large community of developers.
Tron Network also focuses on fostering a vibrant and active community. It has established partnerships with numerous organizations and launched various initiatives to drive adoption and usage of its platform. Furthermore, the network has its own tokenization standard called TRC-20, which enables the creation of tokens on the Tron Network.
In conclusion, Tron Network is a blockchain platform that aims to revolutionize the entertainment industry by providing a decentralized ecosystem for content sharing. With its high scalability, developer-friendly tools, and active community, Tron Network is positioned as a significant player in the blockchain space.
Overview of Ethereum

Ethereum is a decentralized open-source blockchain platform that was first proposed by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 and development began in early 2014. It is designed to enable the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) on its platform. Ethereum works on a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm, similar to Bitcoin, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
One of the key features of Ethereum is its ability to support Turing-complete smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code. These smart contracts can be used to automate a wide range of decentralized applications, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), decentralized exchanges, and decentralized social networks.
Ethereum has its native cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH), which is used to pay for transaction fees and to incentivize miners to validate transactions. ETH is currently the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, after Bitcoin.
Another important aspect of Ethereum is its robust developer community and ecosystem. Ethereum has a wide range of developer tools and programming languages, making it easier for developers to build and deploy DApps on the platform. This has led to a rapid growth in the number of decentralized applications and tokens built on Ethereum.
However, Ethereum has faced scalability challenges due to its current PoW consensus algorithm. The network has been congested during periods of high demand, resulting in high gas (transaction) fees and slow transaction processing times. To address this, Ethereum has been working on transitioning to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm called Ethereum 2.0, which aims to improve scalability and sustainability.
In conclusion, Ethereum is a pioneering blockchain platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications. It has a vibrant developer community and ecosystem, but faces scalability challenges that are being addressed with the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
Comparison of Tron Network and Ethereum
Tron Network and Ethereum are two of the leading blockchain platforms in the world. While they share some similarities, such as being decentralized and based on blockchain technology, they also have several key differences. In this article, we will compare Tron Network and Ethereum across various aspects to provide a comprehensive analysis of these platforms.
| Aspect | Tron Network | Ethereum |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus Mechanism | Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| Smart Contract Language | Solidity | Solidity |
| Transaction Speed | 2000 transactions per second | 15-20 transactions per second |
| Transaction Fees | Free transactions | Variable fees |
| Development Tools | Tron Studio, TronWeb | Remix, Truffle |
| Decentralization | Super Representatives | Decentralized network |
| Use Cases | Decentralized applications (DApps), gaming, content sharing | Decentralized finance (DeFi), DApps |
Overall, Tron Network and Ethereum have their own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different use cases. Tron Network excels in transaction speed and fee-free transactions, making it a preferred choice for high-volume applications such as gaming and content sharing. On the other hand, Ethereum offers a more matured ecosystem with widespread adoption, especially in the field of decentralized finance and general-purpose smart contracts.
Ultimately, the choice between Tron Network and Ethereum depends on the specific requirements of a project and the goals of the developers. Both platforms have their own unique features and communities, which should be carefully considered before making a decision.
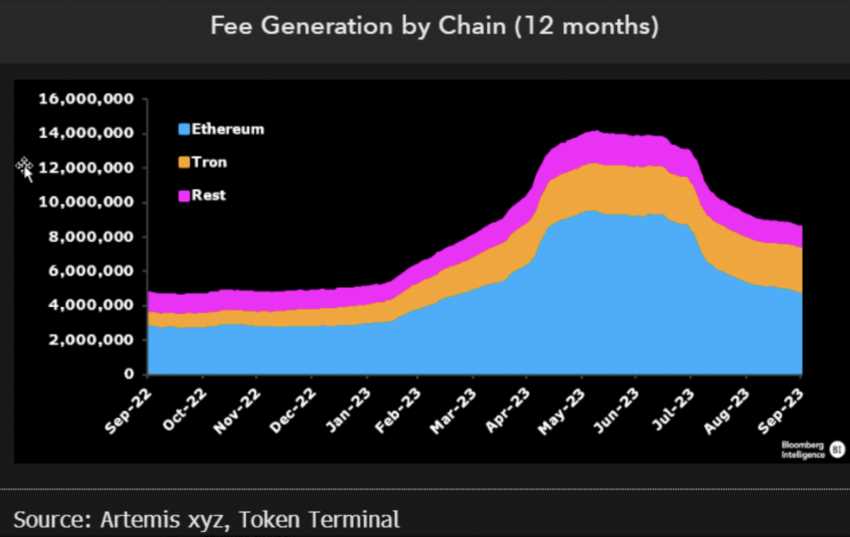
Scalability
Scalability is a crucial factor to consider when comparing blockchain platforms. It refers to the ability of a network to handle an increasing amount of transactions effectively without compromising its performance or security. Both Tron Network and Ethereum have implemented different approaches to address scalability issues.
Tron Network’s Approach to Scalability
Tron Network has taken significant steps to enhance scalability. It uses a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, where a limited number of elected validators validate transactions and create new blocks. This allows Tron Network to achieve a higher throughput compared to Ethereum’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. With a higher throughput, Tron Network can process more transactions per unit of time, resulting in improved scalability.
In addition to DPoS, Tron Network also employs a multi-layer architecture, which enables horizontal scaling. The network is divided into different layers, with each layer responsible for a specific function. This design allows Tron Network to scale horizontally by adding more layers as the demand for transactions increases.
Ethereum’s Approach to Scalability

Ethereum, on the other hand, is in the process of transitioning from a PoW consensus mechanism to a Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism called Ethereum 2.0. This upgrade aims to improve the scalability of the network significantly. PoS, as compared to PoW, is less resource-intensive, allowing for faster transaction validation and a higher throughput.
In addition to transitioning to PoS, Ethereum is exploring Layer 2 solutions to address scalability concerns. These solutions aim to process transactions off-chain and then settle them on the Ethereum mainnet, reducing congestion and increasing the network’s capacity to handle more transactions. Layer 2 solutions like state channels and sidechains have gained traction and are being actively developed within the Ethereum community.
It is worth mentioning that both Tron Network and Ethereum face scalability challenges, but each platform is actively working on addressing these issues. Tron Network’s use of DPoS and multi-layer architecture, combined with Ethereum’s transition to PoS and exploration of Layer 2 solutions, demonstrate their commitment to improving scalability and meeting the growing demands of the blockchain market.
Smart Contracts and DApps

Smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) are key components of both the Tron Network and Ethereum. They play a crucial role in ensuring the transparency and security of transactions on these blockchain platforms.
Smart Contracts

A smart contract is a self-executing digital contract that is stored on the blockchain. It contains the terms and conditions agreed upon by the participating parties and automatically executes the defined actions once the specified conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and ensures trust and efficiency in transactions.
Both Tron and Ethereum support smart contracts, but they use different programming languages. Ethereum uses Solidity, a high-level contract-oriented language, while Tron supports multiple programming languages including Java, Python, and Solidity itself. This gives developers more flexibility in choosing the language they are most comfortable with.
Smart contracts on both platforms are immutable, meaning once deployed, they cannot be altered. This provides transparency and auditability, as anyone can verify the execution of the contract.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
DApps are applications built on top of blockchain networks that utilize smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer interactions. They aim to decentralize traditional centralized systems, providing more transparency, security, and autonomy to users.
Both Tron and Ethereum support the development and deployment of DApps. However, there are some differences in terms of scalability and transaction speed.
Tron employs a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which allows for faster transaction speeds and higher scalability compared to Ethereum’s Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism. This makes Tron a more attractive choice for DApp developers who require quick and frequent transactions.
On the other hand, Ethereum has a larger user base and a more established ecosystem of DApps. It also has the advantage of being the first platform to introduce smart contracts and DApps, which has resulted in many developers and projects building on it.
Ultimately, the choice between Tron and Ethereum for developing DApps depends on the specific requirements of the project. Developers need to consider factors such as transaction speed, scalability, programming language preferences, and existing ecosystem support.
Both Tron and Ethereum are continuously evolving and improving their capabilities to better support smart contracts and DApps. As blockchain technology advances, we can expect more innovative solutions and applications to be built on these platforms.
What is the Tron Network and Ethereum?
The Tron Network and Ethereum are both decentralized blockchain platforms that allow developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts. They have their own native cryptocurrencies: Tron (TRX) and Ether (ETH) respectively.
How are the transaction speeds different between Tron and Ethereum?
Tron boasts a much higher transaction speed compared to Ethereum. Tron can handle up to 2,000 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum can only handle around 15 TPS. This makes Tron more suitable for applications requiring fast and high-volume transactions.
Which blockchain platform has a larger developer community?
As of now, Ethereum has a larger and more established developer community compared to Tron. Ethereum has been around longer and has gained significant popularity due to its early adoption and pioneering role in the blockchain industry.
What are some notable projects built on Tron and Ethereum?
Some notable projects built on Tron include BitTorrent, which was acquired by Tron Foundation, and TRONbet, a popular decentralized gambling application. On the other hand, Ethereum has seen the development of projects such as CryptoKitties, Uniswap, and MakerDAO.