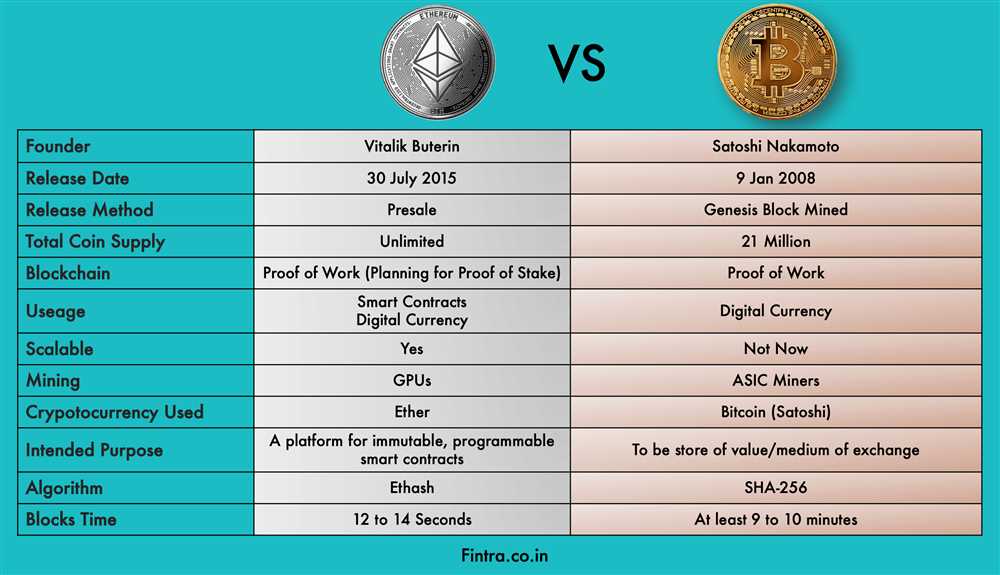
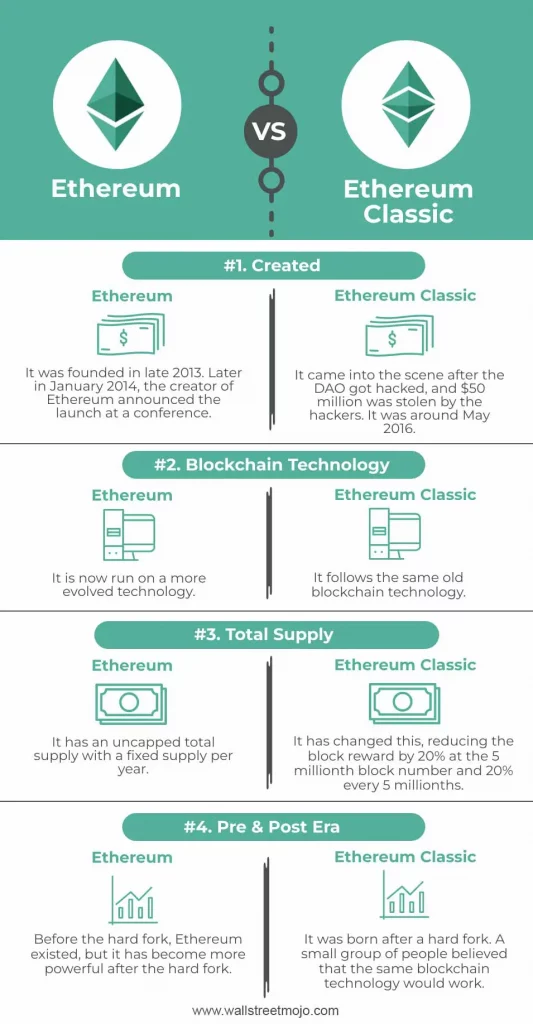
When it comes to blockchain technology, Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri are some of the most prominent platforms that offer various onchain functionalities. While they all operate on the same fundamental concept of distributed ledger technology, there are several key similarities and differences between these three platforms.
Ethereum, often referred to as the “world computer,” is known for its smart contract capabilities and decentralized applications (DApps). It was the first platform to introduce the concept of smart contracts, allowing developers to build and deploy applications that run exactly as programmed without any possibility of downtime, censorship, fraud, or third-party interference. Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH), which is used to pay for computational services and as a means of exchange within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Tron, on the other hand, positions itself as a platform for the entertainment industry. It aims to decentralize the entertainment content distribution system, allowing creators to have more control over their content and its monetization. Tron’s native cryptocurrency is TRX, which is used for transactions and as an incentive mechanism for content creators and users. Tron also supports the creation of DApps and smart contracts, similar to Ethereum, but with a focus on the entertainment sector.
ETKhatri is a newer platform that seeks to combine the best features of Ethereum and Tron while addressing some of their limitations. It aims to provide a more scalable and efficient blockchain solution by utilizing a hybrid consensus mechanism. ETKhatri also emphasizes privacy and security, offering users the ability to conduct transactions and interact with smart contracts in a private and secure manner. Its native cryptocurrency is ETK, which serves as a mode of payment and governance within the ETKhatri ecosystem.
In summary, while Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri share the common goal of utilizing blockchain technology, they differ in their specific focus and implementation. Ethereum pioneered the concept of smart contracts, Tron specializes in entertainment content distribution, and ETKhatri aims to combine the best features of both in a more scalable and secure manner. Understanding these similarities and differences can help users and developers determine which platform best suits their needs and objectives.
Understanding the Similarities and Differences between Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri
Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri are all blockchain platforms that offer similar functionalities but have some key differences that set them apart. Here, we will explore the similarities and differences between these three platforms and how they contribute to their overall onchain functionalities.
One similarity between Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri is that they all support smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They automatically execute when certain conditions are met, providing a transparent and secure way to conduct transactions. This feature is fundamental to all three platforms and enables a wide range of decentralized applications (DApps) to be built on top of them.
Another similarity is that Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri all utilize a decentralized consensus mechanism. Ethereum currently uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm, but it is in the process of transitioning to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm. Tron and ETKhatri both use a delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which involves a set of elected representatives who validate transactions and secure the network. This decentralized consensus ensures the reliability, security, and immutability of the blockchain.
Despite these similarities, Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri have distinct differences that make each platform unique. Ethereum is known for being the first platform to introduce smart contracts and has the largest developer community and ecosystem. It also has a higher transaction fee and slower transaction speed compared to Tron and ETKhatri.
Tron, on the other hand, focuses on providing a highly scalable and high-performance blockchain platform. It boasts high transaction speeds and lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum. Tron also places a strong emphasis on content distribution and entertainment applications, making it popular within the gaming and media industries.
ETKhatri, a relatively newer platform, aims to combine the best features of Ethereum and Tron while also addressing their limitations. ETKhatri is designed to provide high-speed transactions, low transaction fees, and scalable infrastructure. It also integrates smart contracts and aims to attract developers from both Ethereum and Tron ecosystems.
In conclusion, Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri are all blockchain platforms that offer similar functionalities but have distinct differences. While they all support smart contracts and decentralized consensus, Ethereum has a larger developer community and ecosystem, Tron focuses on high scalability and content distribution, and ETKhatri aims to combine the best features of both Ethereum and Tron. Understanding these similarities and differences can help users choose the platform that best suits their needs and goals.
Onchain Functionalities Overview
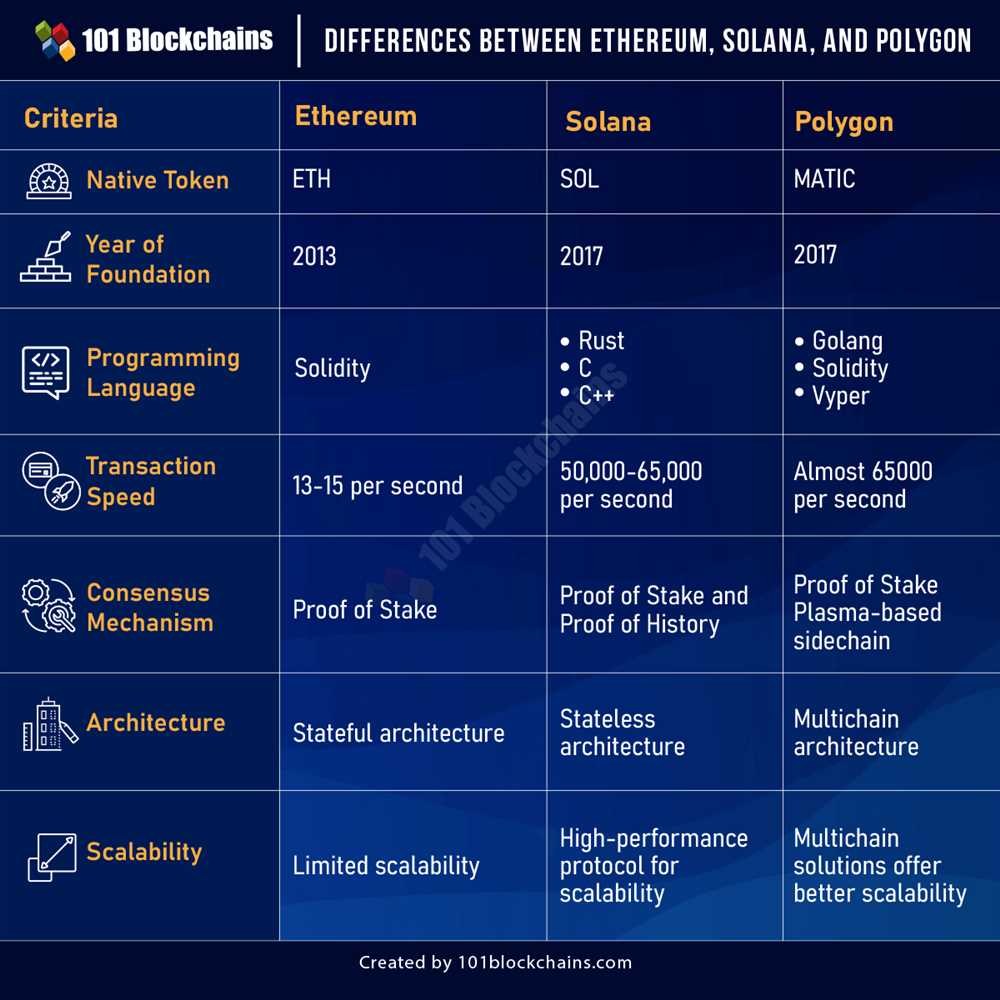
Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri are three blockchain platforms that offer a wide range of onchain functionalities. While they share similarities in terms of their ability to execute smart contracts and host decentralized applications (DApps), there are also notable differences in their design and capabilities.
Smart Contract Execution

All three platforms support smart contract execution, which allows for the creation and enforcement of self-executing agreements. Ethereum, being the first and most well-known platform, has a more mature ecosystem and a larger number of smart contracts deployed on its network. Tron and ETKhatri, on the other hand, have been developed more recently and are still building their own communities and developer base.
Scalability and Performance
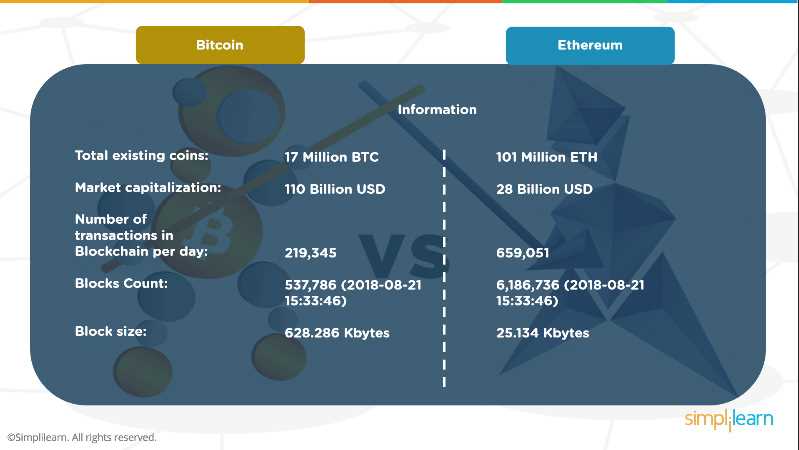
Scalability is a crucial factor for blockchain platforms, as it determines their ability to handle a large number of transactions. Ethereum currently faces scalability challenges due to its limited transaction processing capacity, resulting in network congestion and high transaction fees. Tron and ETKhatri, on the other hand, have implemented different consensus mechanisms and scalability solutions to improve their performance and overall user experience.
Tron utilizes a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which allows for faster block confirmation times and higher transaction throughput compared to Ethereum. ETKhatri, on the other hand, uses a unique consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Value, which combines the advantages of proof-of-work and proof-of-stake to achieve high transaction processing speeds and scalability.
Decentralized Application (DApp) Development

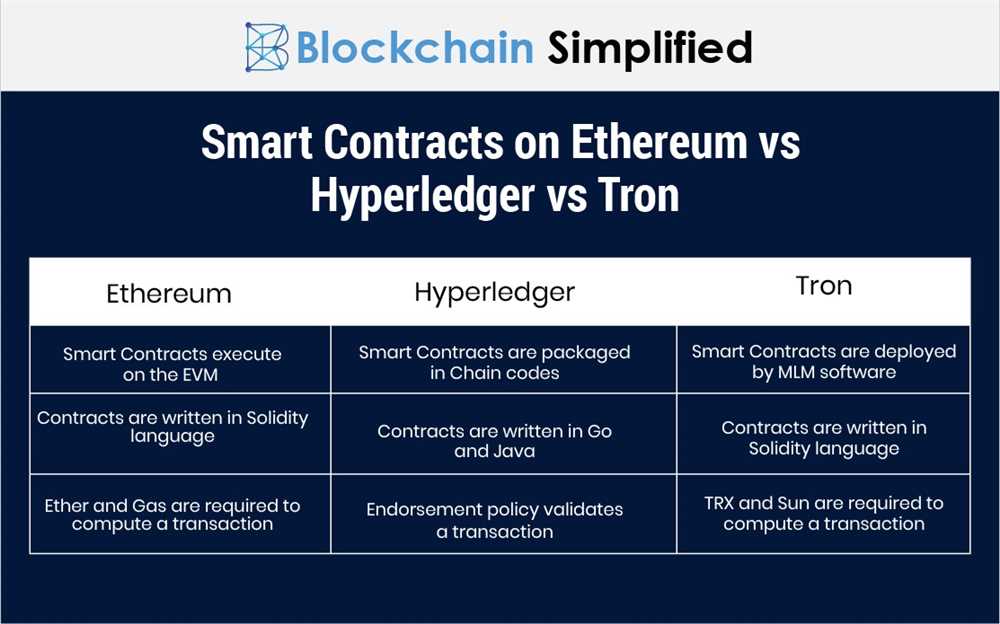
All three platforms provide developers with tools and frameworks to build decentralized applications (DApps). Ethereum’s Solidity programming language is widely adopted and offers a rich set of features for smart contract development. Tron and ETKhatri also provide their own programming languages (TronScript and ETKScript, respectively) and development environments to facilitate DApp creation.
Furthermore, Tron and ETKhatri emphasize DApp usability and user experience by offering features such as easy account creation, on-chain governance mechanisms, and seamless integration with existing web technologies. This makes it easier for developers to attract users and build successful DApps on their respective platforms.
Interoperability and Integration
Interoperability and integration capabilities are crucial for blockchain platforms, as they allow for seamless communication and data exchange between different networks. Ethereum currently has the most extensive ecosystem with various projects and protocols built on top of its blockchain. This allows for easy integration with other projects and enhances the overall interoperability of the platform.
Tron and ETKhatri have also made efforts to improve interoperability by implementing support for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This enables developers to port existing Ethereum DApps onto their platforms with minimal modifications. Tron has also introduced the TronGrid protocol, which provides developers with an API gateway to interact with the Tron network and off-chain resources.
Conclusion
While Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri offer similar onchain functionalities, they differ in terms of scalability, performance, developer experience, and interoperability. The choice of platform depends on the specific requirements of the project and the intended use case. Developers and businesses should carefully evaluate these factors to determine the most suitable platform for their needs.
Ethereum: Smart Contracts and DeFi

Ethereum is a blockchain-based platform that enables the creation and execution of smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code. They automatically execute transactions when the conditions specified in the code are met.
One of the key functionalities of Ethereum is its ability to support decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. DeFi refers to the use of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies to recreate traditional financial systems, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, without the need for intermediaries like banks.
Ethereum’s smart contracts enable the creation of various DeFi protocols, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending platforms, and stablecoins. These protocols allow users to trade assets, borrow and lend cryptocurrencies, and earn interest on their holdings, all without relying on centralized institutions.
Some popular decentralized applications (dApps) built on Ethereum include Uniswap, a leading decentralized exchange, Compound, a lending and borrowing platform, and MakerDAO, the creator of the stablecoin DAI. These dApps leverage the smart contract capabilities of Ethereum to provide users with decentralized and automated financial services.
Ethereum’s programmable smart contracts and open-source nature make it a popular choice for developers looking to build decentralized applications and create new financial products. It has become the dominant platform for DeFi, with a wide range of projects and protocols being built on top of it.
However, Ethereum has faced scalability challenges, with high gas fees and network congestion during periods of high demand. This has led to the development of competing blockchain platforms, such as Tron and ETKhatri, which aim to address these scalability issues while providing similar functionalities.
Despite the challenges, Ethereum remains a fundamental platform for smart contracts and DeFi, playing a pivotal role in the ongoing evolution of the blockchain industry.
Tron: DApps and Scalability
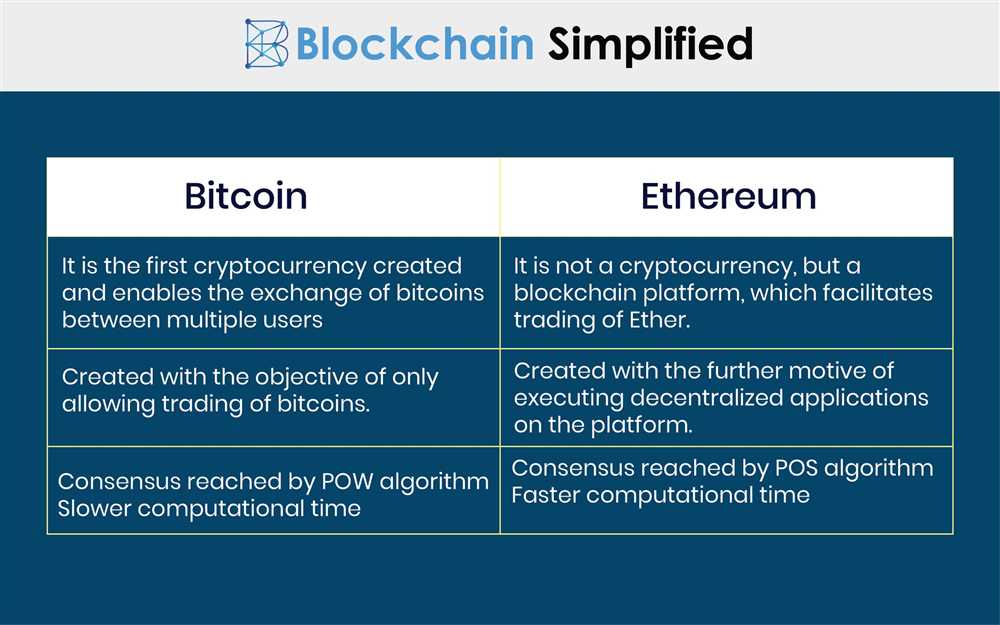
Tron, similar to Ethereum and ETKhatri, is a blockchain network that supports the development and deployment of decentralized applications (DApps). However, Tron is known for its focus on scalability and high transaction throughput.
Scalability is a crucial factor in the success of any blockchain platform. With the increasing usage of DApps and the growing demand for fast and efficient transactions, Tron has implemented several measures to improve its scalability.
Scalability Solutions
Tron introduced the concept of a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) consensus algorithm, which allows for faster block confirmation times and higher transaction throughput compared to traditional proof-of-work (PoW) algorithms. This means that Tron can process a higher number of transactions per second, making it more scalable.
In addition to DPoS, Tron has implemented a technology called Sun Network. Sun Network is a second-layer scaling solution that aims to enhance the overall performance of the Tron network by addressing scalability issues. It introduces features such as sidechains, cross-chain communication, and optimized transaction processing, which further improve the scalability of Tron’s blockchain platform.
DApp Development on Tron

Tron provides developers with a robust set of tools and resources to build and deploy DApps on its network. The Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) is a key component that allows developers to write smart contracts in programming languages such as Solidity and deploy them on the Tron blockchain.
Tron also offers the TronGrid API, which provides developers with access to various features and functionalities of the Tron blockchain, making it easier for them to create and interact with DApps.
Furthermore, Tron has a vast and active community, which includes developers, enthusiasts, and users, who contribute to the growth and adoption of DApps on the Tron network. This vibrant ecosystem further enhances the development and availability of innovative DApps on Tron.
ETKhatri: Privacy and Decentralization

ETKhatri is a blockchain platform that prioritizes privacy and decentralization in its on-chain functionalities. It aims to provide users with a secure and private environment for conducting transactions and interacting with decentralized applications (dApps).
Privacy Features
ETKhatri incorporates several features to ensure user privacy:
- Confidential Transactions: ETKhatri uses confidential transactions to hide the transaction amounts, ensuring that the financial details of users remain private.
- Ring Signature: The platform utilizes ring signature technology to enhance privacy by mixing the user’s transaction with others, making it difficult to trace the origins of a particular transaction.
- Stealth Address: ETKhatri also employs stealth addresses, which enable users to generate unique addresses for each transaction, making it challenging to associate the sender and the recipient.
Decentralization

ETKhatri is designed to be a decentralized platform, ensuring that power and control are distributed among its network participants. This decentralization is achieved through:
- Consensus Mechanism: ETKhatri relies on a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism, allowing validators to agree on the validity of transactions and maintain the network’s integrity without the need for a central authority.
- P2P Network: The platform operates on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, where nodes communicate directly with each other, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enabling a trustless environment.
- Open Source Code: ETKhatri’s codebase is open source, meaning that anyone can inspect, review, and contribute to the development of the platform. This transparency fosters trust and ensures that the platform can evolve with the input of a diverse community.
In summary, ETKhatri places a strong emphasis on privacy and decentralization, making it an appealing choice for users who value these attributes in a blockchain platform. With its privacy features and decentralized architecture, ETKhatri offers a secure and private environment for users to engage with the blockchain and dApps.
What are the main similarities between Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri in their onchain functionalities?
Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri are all blockchain platforms that allow for the creation and execution of smart contracts. They all enable developers and users to build and deploy decentralized applications (DApps) on their respective networks. Additionally, they support the use of their native tokens as a means of exchange and as fuel for executing smart contracts.
How do Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri differ in their onchain functionalities?
While Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri share similarities in their onchain functionalities, there are also key differences. Ethereum is the most established and widely used platform, known for its robustness and extensive developer community. Tron, on the other hand, focuses on high scalability and fast transactions. ETKhatri, being a relatively new and lesser-known platform, might have its own unique features that set it apart from Ethereum and Tron but requires further research.
What are some use cases for Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri in their onchain functionalities?
Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri can be used for various purposes in their onchain functionalities. Some common use cases include decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and gaming platforms. These platforms provide a secure and transparent environment for developers and users to create and interact with decentralized applications.
Which platform among Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri is better for developing decentralized applications?
The choice of platform for developing decentralized applications depends on various factors such as the specific requirements of the application, the desired level of scalability, and the available resources and tools. Ethereum is well-established and has a large developer community, making it a popular choice. Tron offers high scalability and low transaction fees, which may be advantageous for some applications. ETKhatri might have its own unique features, but more research and evaluation are needed to determine its suitability for DApp development.
What are the transaction fees like on Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri?
The transaction fees on Ethereum, Tron, and ETKhatri can vary. Ethereum has been known for its high transaction fees, especially during periods of high network congestion. Tron, on the other hand, boasts much lower fees and faster transactions. As for ETKhatri, as a lesser-known platform, information about its transaction fees may not be readily available and requires further research.