Comparing Onchain Ethereum and Tron: An Analysis of Their Development

The world of blockchain technology has seen tremendous growth in recent years, with new platforms and cryptocurrencies constantly being developed. Two of the most prominent players in this space are Ethereum and Tron. Both of these platforms have gained significant attention and adoption, but they differ in many aspects. In this article, we will explore the emergence of onchain Ethereum and Tron, and conduct a comparative analysis to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
Ethereum, often hailed as the pioneer of smart contract platforms, has revolutionized the way we think about decentralized applications (dApps). With its robust infrastructure and developer-friendly environment, Ethereum has paved the way for countless projects and tokens to be created. Its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), has established itself as one of the most valuable and widely traded digital assets in the world.
On the other hand, Tron has emerged as a strong competitor to Ethereum, aiming to offer faster and cheaper transactions with its own native cryptocurrency TRX. Tron also boasts a large and active community, and its founder Justin Sun has been successful in securing partnerships with various industry giants. Tron’s goal is to become the go-to platform for dApps and content sharing, offering a decentralized and censorship-resistant environment.
While both Ethereum and Tron offer similar functionalities and support smart contracts, they differ in terms of scalability, transaction speed, and governance. Ethereum has faced scalability issues due to its Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees during periods of high network congestion. Tron, on the other hand, utilizes a delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which allows for faster block generation and higher transaction throughput.
In conclusion, the emergence of onchain Ethereum and Tron has brought about a new era of decentralized applications and blockchain technology. Both platforms have their own unique strengths and weaknesses, and it’s up to developers and users to decide which one best suits their needs. As the industry continues to evolve, it will be fascinating to see how these two platforms compete and collaborate to shape the future of blockchain technology.
Ethereum: A Pioneer of Onchain Technology

Ethereum is one of the most revolutionary blockchain platforms in the world, serving as a pioneer in the development of onchain technology. It was created by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 and formally launched in 2015. Since its inception, Ethereum has played a crucial role in shaping the landscape of decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications
One of the key features of Ethereum is its ability to support smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud or censorship.
Ethereum allows developers to create and deploy decentralized applications (DApps) that run on the blockchain. DApps leverage the power of smart contracts to provide transparent, immutable, and secure solutions for various industries such as finance, supply chain management, and gaming.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)

The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a key component of the Ethereum blockchain. It is a runtime environment that executes smart contracts and enables the interaction of various DApps on the network. The EVM ensures consistency across all nodes in the Ethereum network and facilitates the execution of complex decentralized applications.
Developers can write smart contracts in Ethereum’s native programming language, Solidity, and deploy them on the EVM. This allows for the development of sophisticated applications with complex logic and functionalities.
Advancements in Scalability

While Ethereum has been a pioneer in onchain technology, it has faced challenges in terms of scalability. The network has struggled with high transaction fees and limited throughput, leading to congestion during periods of high demand.
To address these scalability issues, Ethereum has been working on the implementation of various scaling solutions such as Ethereum 2.0 and layer 2 protocols like Optimistic Rollups and zk-rollups. These solutions aim to increase the network’s capacity, reduce transaction fees, and improve the overall user experience.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s contribution to the development of onchain technology cannot be overstated. It has paved the way for the emergence of decentralized applications and smart contracts, offering a decentralized and trustless alternative to traditional centralized systems. As Ethereum continues to innovate and address scalability challenges, it remains at the forefront of the blockchain revolution.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enables the creation of decentralized applications | Scalability challenges |
| Supports smart contracts and self-executing contracts | High transaction fees |
| Transparent, immutable, and secure solutions | Limited throughput |
| Ongoing advancements in scalability |
Tron: An Up-and-Coming Competitor in the Onchain Space
Tron is a blockchain platform that is quickly gaining popularity and emerging as a strong competitor in the onchain space. Founded by Justin Sun in 2017, Tron aims to decentralize the internet by using blockchain technology.
One of the key features of Tron is its focus on providing a decentralized entertainment ecosystem. With Tron, users can create and share content without relying on centralized platforms. This allows for more transparency, as well as greater control and ownership of content for both creators and consumers.
Main Features of Tron
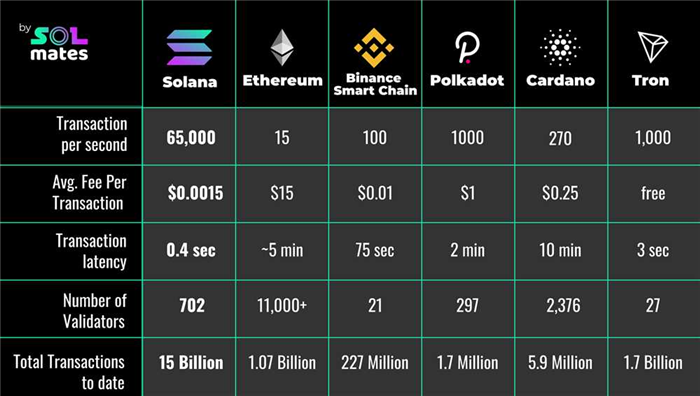
- High Transaction Throughput: Tron has a high transaction throughput, which means it can handle a large number of transactions per second. This scalability is a crucial factor for the success of any onchain platform, as it allows for faster and more efficient processing.
- Smart Contracts: Tron supports smart contract functionality, similar to Ethereum. This enables developers to create decentralized applications (DApps) on the Tron platform, using its own programming language, Solidity.
- TRX Cryptocurrency: TRX is the native cryptocurrency of the Tron platform. It is used for various purposes within the ecosystem, such as paying for transaction fees and incentivizing users to participate in the network.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Tron utilizes a DPoS consensus mechanism, which involves a smaller set of block producers who are elected by token holders to validate transactions. This helps to improve efficiency and reduce the energy consumption associated with mining.
Advantages of Tron

Tron has several advantages that contribute to its growing popularity:
- Strong Community: Tron has a vibrant and active community that supports the platform’s development and growth. This community helps to drive adoption and provides valuable feedback to the Tron team.
- Partnerships and Acquisitions: Tron has formed strategic partnerships with various companies and acquired popular platforms, such as BitTorrent. These partnerships and acquisitions help to expand the Tron ecosystem and attract more users.
- Scalability: Tron’s high transaction throughput and efficient consensus mechanism make it a scalable platform, capable of handling a large number of transactions and supporting widespread adoption.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Tron’s blockchain offers lower transaction costs compared to traditional centralized platforms, making it an attractive option for content creators and consumers.
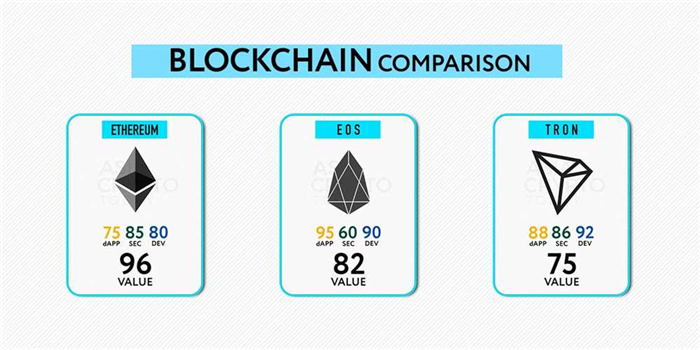
Overall, Tron is positioned as a strong competitor in the onchain space. With its focus on decentralization, scalability, and a rapidly growing community, Tron has the potential to revolutionize the entertainment industry and other sectors that rely on centralized platforms.
A Comparative Look at Onchain Ethereum and Tron
In the world of cryptocurrency, Ethereum and Tron have emerged as two of the most prominent blockchain platforms. Both platforms offer a range of features and capabilities that make them attractive to developers and users alike. However, there are key differences between Ethereum and Tron that make each platform unique.
One of the main differences between Ethereum and Tron lies in their underlying technology. Ethereum is known for its smart contract functionality, which allows developers to create and execute decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum blockchain. This has made Ethereum the platform of choice for many developers looking to build decentralized applications for various use cases.
On the other hand, Tron takes a slightly different approach by focusing on scalability and high transaction throughput. Tron aims to offer a platform that can handle a large number of transactions per second, making it more suitable for applications that require high-speed and high-volume transactions. Tron achieves this through a delegated proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which allows for faster block confirmation times compared to Ethereum’s proof-of-work consensus.
Another notable difference between Ethereum and Tron is their respective ecosystems. Ethereum has a vibrant and active developer community, with a wide range of tools, libraries, and frameworks available for developers to build on top of the Ethereum platform. This has resulted in a large number of DApps being built on the Ethereum blockchain, creating a diverse and thriving ecosystem.
While Tron’s ecosystem is still growing, it has made significant progress in attracting developers and users to its platform. Tron has its own set of tools and resources, such as the Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) and the TronGrid API, which make it easier for developers to create and deploy applications on the Tron network. Additionally, Tron has made efforts to attract popular DApps and projects to its platform, further expanding its ecosystem.
In terms of token economics, both Ethereum and Tron have their native tokens that power their respective platforms. Ethereum’s native token, Ether (ETH), is used for paying transaction fees and executing smart contracts on the Ethereum network. Tron’s native token, TRX, serves a similar purpose, enabling users to pay for transactions and interact with DApps on the Tron network.
Overall, Ethereum and Tron offer unique features and capabilities that make them appealing to different types of users and developers. Ethereum’s focus on smart contracts and decentralized applications has made it a popular choice for developers in the blockchain space, while Tron’s scalability and high transaction throughput make it suitable for applications that require fast and efficient transactions. Ultimately, the choice between Ethereum and Tron depends on the specific requirements and goals of the project at hand.
| Feature | Ethereum | Tron |
|---|---|---|
| Smart contract functionality | Yes | No |
| Scalability | Medium | High |
| Transaction speed | Medium | High |
| Developer community | Active and vibrant | Growing |
| Native token | Ether (ETH) | TRX |
The Future of Onchain Technologies: Ethereum vs Tron

As the world of blockchain technology continues to evolve, two platforms have emerged as frontrunners in the race for onchain dominance: Ethereum and Tron. Both platforms offer unique features and advantages, but which one holds the key to the future of onchain technologies?
Ethereum, the pioneer of smart contract platforms, has established itself as the go-to platform for building decentralized applications (dApps) and launching Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). With a strong developer community and a robust ecosystem of dApps, Ethereum has become the standard for launching new projects and raising funds.
However, Ethereum has faced scalability issues, resulting in slow transaction speeds and high fees. In contrast, Tron aims to solve these problems by utilizing a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, allowing for faster transactions and lower fees. Tron also boasts a solid networking layer and a growing ecosystem of dApps.
While Ethereum has the advantage of being the first mover in the space, Tron has made significant strides in gaining market share and attracting developers and users. Its founder, Justin Sun, has strategically acquired popular dApps like BitTorrent and Steemit, further expanding Tron’s user base and attracting attention from mainstream media.
Another aspect to consider is governance. Ethereum is governed by a decentralized community, with decision-making power distributed among its stakeholders. Tron, on the other hand, is governed by a foundation led by Justin Sun. This centralized governance structure provides Tron with the ability to make quick decisions and implement changes, but it also raises concerns about censorship and centralization.
In conclusion, the future of onchain technologies will likely be shaped by the rivalry between Ethereum and Tron. While Ethereum has the advantage of being the more established platform with a larger developer community, Tron offers faster transaction speeds and lower fees, as well as a more centralized governance structure. It remains to be seen which platform will ultimately prevail, but one thing is certain – both Ethereum and Tron are driving innovation in the blockchain space and paving the way for a decentralized future.
What is the main difference between onchain Ethereum and Tron?
The main difference between onchain Ethereum and Tron is the underlying blockchain technology. Ethereum uses its own blockchain, which is decentralized and highly secure. Tron, on the other hand, uses its own blockchain called the Tron Virtual Machine (TVM). While both platforms support smart contracts and decentralized applications, the implementation and governance of these technologies differ between Ethereum and Tron.
Which platform, Ethereum or Tron, has more decentralized applications (dApps)?
Currently, Ethereum has a larger number of decentralized applications (dApps) compared to Tron. This is mainly because Ethereum has been around longer and has a larger developer community. However, Tron has been gaining popularity and attracting developers with its high scalability and low transaction fees. As a result, the number of dApps on Tron is steadily increasing, and it is expected to catch up with Ethereum in the future.
What are the benefits of onchain Ethereum and Tron?
Onchain Ethereum and Tron offer several benefits compared to traditional centralized systems. Firstly, both platforms provide a high level of security and immutability due to their decentralized nature. This means that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or manipulated. Additionally, both platforms promote transparency and trust through their open-source code and public ledgers. Onchain Ethereum and Tron also enable the development and deployment of smart contracts, which allow for automated and trustless interactions between parties. Overall, these benefits make onchain Ethereum and Tron attractive for various use cases, ranging from financial applications to supply chain management.