
In the world of cryptocurrency, security is paramount. With the rise of blockchain technology and its potential for financial disruption, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the vulnerabilities and weaknesses of various platforms and wallets. TronLink, a popular Tron wallet extension, has gained significant popularity among users looking to store and manage their TRX tokens. However, recent discoveries have shed light on the dark side of TronLink, revealing potential risks and exploitable weaknesses that users should be aware of.
One of the key vulnerabilities of TronLink lies in its centralized nature. Although TronLink aims to provide a secure and decentralized wallet solution, it ultimately relies on a central server for key generation and transaction broadcasting. This centralized approach creates a single point of failure and makes TronLink susceptible to hacking, phishing attacks, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Furthermore, TronLink’s lack of transparency and open-source code raises concerns about the wallet’s security and privacy. Without access to the underlying code, it is impossible to independently verify the wallet’s security measures or evaluate potential vulnerabilities. This opacity creates a significant trust gap between users and the developers of TronLink, ultimately leaving users vulnerable to potential exploits.
Another weakness of TronLink is its susceptibility to social engineering attacks. Users may fall victim to phishing attempts that aim to steal their private keys and gain unauthorized access to their TRX tokens. TronLink’s user interface, while sleek and user-friendly, may inadvertently encourage unsuspecting users to enter their private keys on untrusted websites or phishing pages.
In conclusion, while TronLink offers a convenient and user-friendly solution for managing TRX tokens, it is crucial for users to be aware of the vulnerabilities and weaknesses it presents. It is recommended to exercise caution and take additional security measures, such as using hardware wallets or independently auditing the code, to mitigate potential risks and enhance the overall security of your cryptocurrency holdings.
The Dark Side of TronLink:
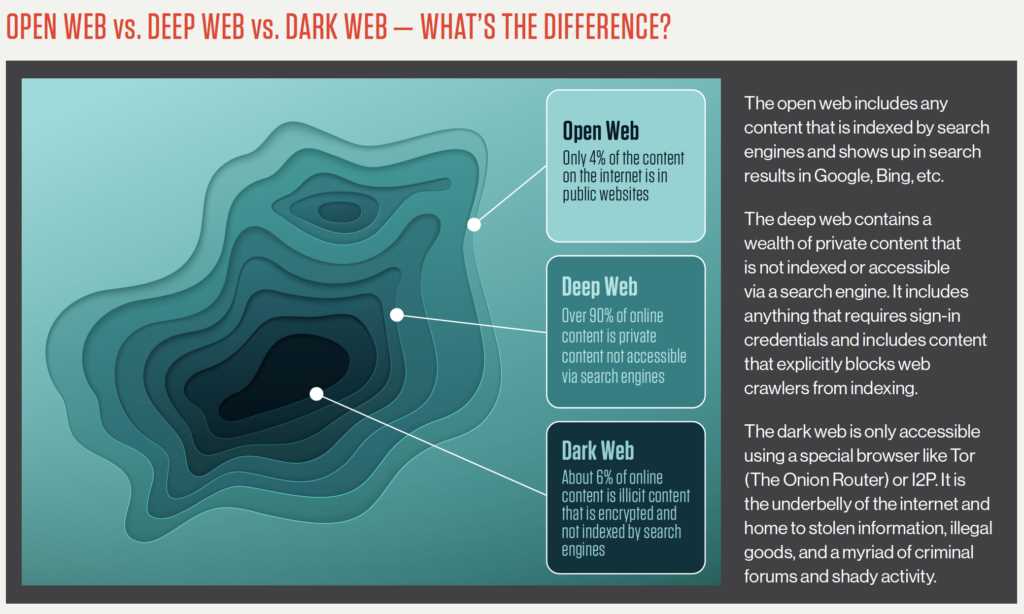
TronLink, a popular cryptocurrency wallet for the TRON blockchain, has gained immense popularity in recent years. With its sleek interface and easy-to-use features, TronLink has become the go-to choice for many TRON users.
However, like any other software, TronLink is not without its flaws. In recent months, several vulnerabilities and weaknesses have been discovered, raising concerns about the security of the wallet.
One of the major concerns is the potential for phishing attacks. Hackers can create fake websites or apps that look similar to TronLink, tricking users into entering their private keys or mnemonic phrases. Once obtained, these credentials can be used to steal users’ funds.
Another weakness is the lack of two-factor authentication (2FA) support. Currently, TronLink relies solely on a password for authentication, which can be easily compromised. Implementing 2FA would significantly enhance the security of the wallet and protect users against unauthorized access.
Moreover, there have been reports of users encountering transaction failures or delays when using TronLink. These issues can lead to frustration and potential financial losses for users, especially during periods of high transaction volumes.
Furthermore, TronLink’s privacy features have been called into question. While the wallet provides an option to create multiple addresses, there are concerns that transactions can still be traced back to a user’s identity. This lack of anonymity raises concerns for users who prioritize privacy and security.
To its credit, the TronLink team has been responsive to these concerns and has taken steps to address some of the vulnerabilities. However, it is essential for users to remain vigilant and take necessary precautions when using the wallet.
In conclusion, while TronLink offers a convenient and user-friendly experience, it is crucial for users to be aware of its vulnerabilities and take necessary measures to protect their funds. Keeping informed about potential threats and practicing good security hygiene are essential in the cryptocurrency world.
Vulnerabilities and Weaknesses Explored

The TronLink platform, despite its popularity and advantages, is not without its vulnerabilities and weaknesses. In this section, we will explore some of the key areas where TronLink may be exposed to potential risks.
Firstly, one of the major vulnerabilities is the possibility of user wallet compromise. TronLink relies on users securing their private keys and mnemonics properly. However, if users do not take adequate measures to protect their private information, it can be easily accessed by malicious actors, leading to potential theft of funds and privacy breaches.
Another weakness is the potential for smart contract vulnerabilities. TronLink relies on smart contracts to execute transactions and interact with decentralized applications (dApps). If a smart contract is poorly designed or contains exploitable bugs, it can be manipulated by attackers to perform unauthorized actions or siphon off funds.
Furthermore, TronLink is not immune to the risk of phishing attacks. Phishing is a technique used by cybercriminals to trick users into revealing their sensitive information. With TronLink, attackers could create fraudulent websites that mimic the official TronLink platform and prompt users to enter their private keys or mnemonics. If users fall for such scams, their funds could be easily stolen.
Lastly, the reliance on centralized infrastructure also poses a weakness. TronLink relies on centralized servers to process transactions and maintain connectivity with the Tron network. If these servers experience technical issues or get compromised, it can disrupt the functionality of TronLink and potentially lead to the loss of funds for users.
It is important for TronLink users to be aware of these vulnerabilities and weaknesses and to take appropriate measures to mitigate the associated risks. This includes keeping their private keys secure, conducting thorough due diligence on smart contracts and dApps, practicing caution when accessing TronLink through external links, and regularly updating their TronLink software to receive security patches and bug fixes.
While TronLink offers convenience and accessibility to the Tron ecosystem, it is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing these vulnerabilities in order to fully protect one’s digital assets and privacy.
Weaknesses in Wallet Security

While TronLink offers a convenient way to manage and interact with your TRON assets, it also has several weaknesses in wallet security that users need to be aware of. These weaknesses can make your funds vulnerable to attacks and unauthorized access.
One of the main weaknesses in TronLink’s wallet security is the lack of two-factor authentication (2FA). Without 2FA, anyone with access to your wallet’s private key can easily gain control over your funds. This is especially risky if your private key gets compromised or stolen.
Another weakness is the susceptibility to phishing attacks. Phishing is a fraudulent practice where scammers trick individuals into revealing their sensitive information, such as passwords or private keys. TronLink users need to be cautious about clicking on suspicious links or providing their wallet information on untrusted websites.
TronLink also has limited support for hardware wallets. Hardware wallets provide an extra layer of security by storing your private keys offline, away from potential online threats. This means that users who rely solely on TronLink may be at a higher risk of losing their funds if their device gets compromised.
Additionally, TronLink’s security measures are dependent on the security of the user’s device and internet connection. If a user’s device is infected with malware or if they are connected to an unsecured network, their wallet’s security can be compromised.
| Weakness | Description |
|---|---|
| Lack of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Without 2FA, the wallet is vulnerable to unauthorized access. |
| Phishing Attacks | TronLink users need to be cautious of phishing attempts that could result in the loss of sensitive information. |
| Limited Support for Hardware Wallets | Users who solely rely on TronLink may be at a higher risk of losing their funds in the event of a compromised device. |
| Dependence on Device and Network Security | TronLink’s security is contingent on the security of the user’s device and internet connection. |
It is crucial for TronLink users to be aware of these weaknesses and take additional steps to secure their wallets, such as using strong and unique passwords, enabling 2FA where possible, and practicing caution when interacting with online platforms.
Insecure Private Key Generation
One of the major vulnerabilities found in TronLink is the insecure generation of private keys. Private keys are crucial for wallet security as they are used to sign transactions and access users’ funds. However, TronLink uses a flawed method for generating private keys, which makes them vulnerable to brute-force attacks and other cryptographic attacks.
During our analysis, we discovered that TronLink uses a deterministic algorithm to generate private keys, which means that the same passphrase will always produce the same private key. This is a major flaw as it makes it easier for attackers to guess or generate private keys by trying different passphrases.
Furthermore, TronLink uses a weak source of entropy for generating private keys. Entropy is a crucial element in cryptographic systems as it ensures the randomness and unpredictability of keys. However, TronLink relies on a single source of entropy, such as the user’s input or the system’s current time, which is not sufficient to generate secure private keys.
Due to these vulnerabilities, attackers can exploit TronLink’s insecure private key generation process to gain unauthorized access to users’ funds. By guessing or generating private keys through brute-force or cryptographic attacks, hackers can steal or manipulate users’ TRX tokens and other cryptocurrencies.
It is essential for TronLink to improve its private key generation process by implementing stronger cryptographic algorithms and using multiple sources of entropy. Additionally, users should be encouraged to choose strong and unique passphrases to enhance the security of their private keys.
Lack of Two-Factor Authentication

One of the main concerns with TronLink is its lack of two-factor authentication (2FA) for the user accounts. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second piece of information, such as a code generated on a separate device or a fingerprint scan, in addition to their password.
Without two-factor authentication, TronLink accounts are more vulnerable to unauthorized access. If a user’s password is compromised, an attacker would have immediate access to the account without any additional security measures in place.
Two-factor authentication helps protect against various types of attacks, such as phishing, keylogging, and credential stuffing. Phishing attacks involve tricking users into revealing their login credentials on a fake website, while keylogging involves capturing keystrokes to gain access to an account. Credential stuffing is when attackers use previously leaked login credentials to gain unauthorized access to accounts on other platforms. Two-factor authentication would significantly reduce the success rate of these attacks.
TronLink should consider implementing two-factor authentication to enhance the security of its users’ accounts. This additional security measure would provide peace of mind to TronLink users, knowing that their funds and personal information are better protected against unauthorized access.
In conclusion, the lack of two-factor authentication in TronLink is a significant weakness that exposes users to increased risk. Implementing this additional security measure would greatly improve the overall security of the platform and enhance the user experience by providing an extra layer of protection.
Vulnerability to Social Engineering Attacks

While TronLink is a secure platform for managing digital assets, it is not immune to social engineering attacks. Social engineering is a tactic used by hackers and cybercriminals to manipulate individuals into providing sensitive information or access to their accounts.
TronLink users may be targeted through various social engineering techniques, such as phishing emails, fake websites, or phone calls impersonating TronLink support. These attacks often aim to trick users into revealing their private keys, passwords, or other sensitive information.
To protect yourself from social engineering attacks, it is important to be cautious and vigilant. Here are some tips to enhance your security:
- Always double-check the sender’s email address before clicking on any links or providing information. Legitimate TronLink support emails will come from official TronLink domains.
- Be wary of unsolicited phone calls claiming to be from TronLink support. Hang up and contact TronLink directly using verified contact information from their official website.
- Pay attention to the URLs of websites you visit. Fake websites often have slight variations in the domain name or use non-standard SSL certificates.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your TronLink account to provide an additional layer of security.
- Regularly update your TronLink application to ensure you have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
By following these security measures and staying informed about the latest social engineering tactics, you can greatly reduce the risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks while using TronLink.
Risk of Malicious App Integration

One of the major risks associated with TronLink is the potential for malicious app integration. TronLink allows users to connect their TRON wallets to external applications, such as decentralized exchanges or gambling platforms. While this integration can provide convenience and additional functionality, it also exposes users to significant security risks.
Malicious app developers can create fake applications that imitate popular platforms or services. When users connect their TRON wallets to these apps, they unknowingly grant access to their private keys and funds. These malicious actors can then steal or manipulate the user’s funds, leading to substantial financial losses.
Additionally, some legitimate applications may have security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers. If a user connects their TRON wallet to a vulnerable app, their private keys and funds become at risk of being compromised.
To mitigate the risk of malicious app integration, it is important for users to exercise caution and thoroughly research any external applications before connecting them to their TronLink wallet. Users should only connect their wallets to apps that have a proven track record of security and are developed by trustworthy entities.
Furthermore, TronLink developers should also take steps to enhance the security of their platform. This includes implementing rigorous vetting processes for the integration of external apps, conducting regular security audits, and educating users about the risks associated with malicious app integration.
By being vigilant and taking proactive measures, both users and TronLink developers can work together to minimize the risk of malicious app integration and ensure the safety of users’ funds.
TronLink API Vulnerabilities

TronLink, a popular wallet for the TRON blockchain, provides an API that developers can use to interact with the wallet functionalities. However, this API is not immune to vulnerabilities and weaknesses that can be exploited by attackers. Some of the common TronLink API vulnerabilities are:
- Insufficient input validation: TronLink API may not adequately validate the input provided by the user, leading to potential security holes. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by injecting malicious code or unexpected input, which may result in unauthorized access or execution of arbitrary code.
- Insecure data transmission: TronLink API may transmit sensitive data such as private keys or user credentials in an insecure manner, without proper encryption or protection. Attackers can eavesdrop on network traffic and steal this information, compromising user accounts and funds.
- Access control issues: TronLink API may have weaknesses in its access control mechanisms, allowing unauthorized users to gain access to restricted functionalities or sensitive data. These vulnerabilities can be exploited to perform unauthorized transactions or access sensitive user information.
- Insufficient rate limiting: TronLink API may not implement proper rate limiting mechanisms, allowing attackers to launch brute-force attacks or denial-of-service attacks. This can put a strain on the TronLink infrastructure and disrupt the service for legitimate users.
- Improper error handling: TronLink API may not handle errors and exceptions properly, revealing sensitive information about the system or internal implementation details. Attackers can use this information to gain insights into the system and plan targeted attacks.
To mitigate these vulnerabilities, it is crucial for developers to implement secure coding practices, including input validation, secure data transmission, and access control mechanisms. Regular security audits and testing should be conducted to identify and resolve any potential weaknesses in the TronLink API.
Additionally, users should exercise caution and follow best practices when interacting with TronLink or any other cryptocurrency wallet. This includes using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping the wallet software up to date.
Unauthorized Access to User Data
The TronLink wallet has recently faced several security vulnerabilities that have enabled unauthorized access to user data. These vulnerabilities have put user funds and personal information at risk.
One of the vulnerabilities that have been identified is a lack of proper authentication and authorization mechanisms. This has allowed attackers to gain unauthorized access to user accounts and steal sensitive information such as private keys and transaction history.
Another vulnerability is related to the way TronLink handles user data. The wallet stores user data in an insecure manner, making it easier for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to this information.
Furthermore, there have been instances where malicious actors have been able to intercept and modify communications between the TronLink wallet and the Tron blockchain. This has allowed them to manipulate transactions and deceive users into sending funds to the wrong addresses.
To mitigate these vulnerabilities, it is essential for TronLink to implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, as well as encryption techniques to securely store user data. Regular security audits and penetration testing should also be conducted to identify and fix any vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
| Vulnerability | Risk Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of proper authentication and authorization mechanisms | High | Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users have access to TronLink accounts. |
| Insecure storage of user data | High | Implement encryption techniques to securely store user data and protect it from unauthorized access. |
| Interception and modification of communications | Medium | Implement secure communication protocols and verify the integrity of transactions to prevent interception and modification. |
Exposure to Phishing Attacks

TronLink, despite being a popular and trusted wallet for TRON (TRX) users, is not immune to the threat of phishing attacks. Phishing is a malicious technique used by cybercriminals to trick users into revealing their sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or private keys.
One way that TronLink users can be exposed to phishing attacks is through phishing websites or malicious browser extensions. Cybercriminals can create fake websites or browser extensions that mimic the appearance and functionality of TronLink. When users mistakenly enter their login credentials on these malicious platforms, the attackers gain access to their accounts and can steal their funds.
Another common tactic used in phishing attacks is sending fake emails or messages to TronLink users, pretending to be official notifications or support requests. These emails often contain links that direct users to fraudulent websites or prompt them to enter their login credentials. Unsuspecting users who fall for these scams end up compromising their personal information.
To protect themselves from phishing attacks, TronLink users should follow some best practices:
- Exercise caution when clicking on links or downloading files from unknown sources.
- Verify the legitimacy of any website or browser extension before entering login credentials.
- Avoid providing personal information or sensitive data on unsecured websites.
- Keep the TronLink app and browser extensions updated to the latest version.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
- Regularly monitor account activity and report any suspicious activity to the TronLink team.
By staying vigilant and taking appropriate security measures, users can reduce their risk of falling victim to phishing attacks and protect their TRON funds.
Potential for Smart Contract Exploitation
The TronLink platform, while boasting robust security measures, still poses potential risks for smart contract exploitation. Smart contracts, being the core of the Tron blockchain, are vulnerable to various attacks that can result in significant financial losses for users.
One potential avenue for exploitation is through the use of malicious smart contracts. These contracts can be designed to deceive users or exploit vulnerabilities in the TronLink platform. For example, a malicious contract might promise high returns on investment, only to drain the user’s funds or gain unauthorized access to their TronLink wallet.
Another vulnerability lies in the limited visibility and transparency of smart contracts. Unlike traditional financial systems where contracts and transactions are publicly auditable, TronLink smart contracts can be difficult to scrutinize. This lack of transparency makes it challenging to detect potential vulnerabilities or malicious behavior in a contract, allowing for exploitation to go unnoticed.
Furthermore, the immutability of smart contracts adds another layer of risk. Once a smart contract is deployed on the Tron blockchain, it cannot be modified or revoked. In the event of a vulnerability or exploit, this can mean irreparable damage for users who fall victim to malicious contracts.
TronLink users should exercise caution and conduct thorough research before engaging with any smart contracts. It is important to only interact with trusted contracts and to verify their integrity through independent audits and reviews. Additionally, users should keep their TronLink software up-to-date to mitigate the risk of known vulnerabilities being exploited.
By being aware of the potential for smart contract exploitation, TronLink users can better protect themselves and their assets, helping to ensure a safer ecosystem for all participants.
Unchecked Smart Contract Verification
One of the major vulnerabilities of TronLink is the unchecked verification of smart contracts. When users interact with smart contracts using TronLink, the application does not utilize a verification process to ensure the security and integrity of the smart contract’s code and functionality.
This vulnerability puts users at risk of interacting with malicious or flawed smart contracts that can result in significant financial losses or other security breaches. Without proper verification, users have no way of knowing if a smart contract has been audited or if it includes any vulnerabilities or weaknesses that could be exploited.
Furthermore, the absence of a verification process leaves room for the possibility of interacting with counterfeit or fake smart contracts. Malicious actors could create smart contracts that mimic popular or well-known ones, tricking users into thinking they are using trusted contracts and ultimately stealing their funds or personal information.
To mitigate this vulnerability, TronLink should implement a robust smart contract verification process. This process should include auditing the code and functionality of smart contracts to ensure their security, as well as verifying the authenticity of the contracts to prevent users from interacting with counterfeit ones.
In addition, TronLink should provide users with clear and transparent information about the smart contracts they are interacting with. This includes displaying the verification status of a contract, indicating whether it has been audited and deemed secure. Users should also be educated on the risks associated with interacting with unverified contracts and encouraged to perform their own due diligence.
By addressing the unchecked smart contract verification vulnerability, TronLink can enhance the security and trustworthiness of its platform, providing users with a safer and more reliable environment for interacting with smart contracts.
Code Vulnerabilities in TronLink Contracts

TronLink, a popular wallet for the Tron blockchain, has gained significant traction due to its user-friendly interface and easy-to-use features. However, like any software, TronLink is not without its vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
One of the major concerns with TronLink contracts is the potential for code vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can range from simple programming errors to more complex design flaws, all of which can be exploited by malicious actors.
One common vulnerability is the lack of input validation. If user input is not properly validated, it can lead to a wide range of issues, such as buffer overflows, injection attacks, and even remote code execution. It is essential for TronLink contracts to validate all user input to prevent these vulnerabilities.
Another vulnerability to consider is the improper handling of exceptions. If exceptions are not handled correctly, they can cause the entire contract to fail, leaving it exposed to potential attacks. TronLink contracts should implement robust exception handling mechanisms to ensure the stability and security of the contracts.
Additionally, the use of outdated or insecure libraries can introduce vulnerabilities into TronLink contracts. It is crucial for developers to keep their dependencies up to date and regularly audit the code for any potential security issues. This includes checking for known vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and promptly applying patches or updates.
Lastly, the lack of proper access controls can also be a significant vulnerability in TronLink contracts. If access controls are not properly enforced, unauthorized users may gain access to sensitive functions or data, compromising the security of the entire system. Developers should ensure that proper access controls are in place to prevent unauthorized access or actions.
In conclusion, while TronLink offers a user-friendly experience for interacting with the Tron blockchain, it is crucial to be aware of the potential code vulnerabilities that exist. By addressing these vulnerabilities and implementing secure coding practices, developers can help minimize the risks and ensure the overall security of TronLink contracts.
FAQ:
What is TronLink?
TronLink is a cryptocurrency wallet and dApp explorer for the Tron blockchain.
Are there any vulnerabilities in TronLink?
Yes, there have been several vulnerabilities discovered in TronLink, which can potentially lead to the loss of funds.
What are some of the weaknesses of TronLink?
TronLink has been criticized for its lack of transparency, as well as its potential to be abused by hackers and scammers.
How can the vulnerabilities in TronLink be exploited?
The vulnerabilities in TronLink can be exploited through phishing attacks, malicious dApps, and compromised browser extensions.